Truncated tetraapeirogonal tiling
| Truncated tetraapeirogonal tiling | |
|---|---|
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic uniform tiling |
| Vertex configuration | 4.8.∞ |
| Schläfli symbol | tr{∞,4} or |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 ∞ 4 | |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [∞,4], (*∞42) |
| Dual | |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive |
In geometry, the truncated tetraapeirogonal tiling is a semiregular tiling of the hyperbolic plane. There are one square, one octagon, and one apeirogon on each vertex. It has Schläfli symbol of tr{∞,4}.
Related polyhedra and tilings[]
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [∞,4] family | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |
| {∞,4} | t{∞,4} | r{∞,4} | 2t{∞,4}=t{4,∞} | 2r{∞,4}={4,∞} | rr{∞,4} | tr{∞,4} | |
| Dual figures | |||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |
| V∞4 | V4.∞.∞ | V(4.∞)2 | V8.8.∞ | V4∞ | V43.∞ | V4.8.∞ | |
| Alternations | |||||||
| [1+,∞,4] (*44∞) |
[∞+,4] (∞*2) |
[∞,1+,4] (*2∞2∞) |
[∞,4+] (4*∞) |
[∞,4,1+] (*∞∞2) |
[(∞,4,2+)] (2*2∞) |
[∞,4]+ (∞42) | |
= |
= |
||||||
| h{∞,4} | s{∞,4} | hr{∞,4} | s{4,∞} | h{4,∞} | hrr{∞,4} | s{∞,4} | |

|

|

|

| ||||
| Alternation duals | |||||||

|

|
||||||
| V(∞.4)4 | V3.(3.∞)2 | V(4.∞.4)2 | V3.∞.(3.4)2 | V∞∞ | V∞.44 | V3.3.4.3.∞ | |
| *n42 symmetry mutation of omnitruncated tilings: 4.8.2n | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n42 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||
| *242 [2,4] |
*342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] | |
| Omnitruncated figure |
 4.8.4 |
 4.8.6 |
 4.8.8 |
 4.8.10 |
 4.8.12 |
 4.8.14 |
 4.8.16 |
 4.8.∞ |
| Omnitruncated duals |
 V4.8.4 |
 V4.8.6 |
 V4.8.8 |
 V4.8.10 |
 V4.8.12 |
 V4.8.14 |
 V4.8.16 |
 V4.8.∞ |
| *nn2 symmetry mutations of omnitruncated tilings: 4.2n.2n | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *nn2 [n,n] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||||||||
| *222 [2,2] |
*332 [3,3] |
*442 [4,4] |
*552 [5,5] |
*662 [6,6] |
*772 [7,7] |
*882 [8,8]... |
*∞∞2 [∞,∞] | |||||||
| Figure | 
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

| ||||||
| Config. | 4.4.4 | 4.6.6 | 4.8.8 | 4.10.10 | 4.12.12 | 4.14.14 | 4.16.16 | 4.∞.∞ | ||||||
| Dual | 
|

|

|

|

|

|
|

| ||||||
| Config. | V4.4.4 | V4.6.6 | V4.8.8 | V4.10.10 | V4.12.12 | V4.14.14 | V4.16.16 | V4.∞.∞ | ||||||
Symmetry[]
The dual of this tiling represents the fundamental domains of [∞,4], (*∞42) symmetry. There are 15 small index subgroups constructed from [∞,4] by mirror removal and alternation. Mirrors can be removed if its branch orders are all even, and cuts neighboring branch orders in half. Removing two mirrors leaves a half-order gyration point where the removed mirrors met. In these images fundamental domains are alternately colored black and white, and mirrors exist on the boundaries between colors. The subgroup index-8 group, [1+,∞,1+,4,1+] (∞2∞2) is the commutator subgroup of [∞,4].
A larger subgroup is constructed as [∞,4*], index 8, as [∞,4+], (4*∞) with gyration points removed, becomes (*∞∞∞∞) or (*∞4), and another [∞*,4], index ∞ as [∞+,4], (∞*2) with gyration points removed as (*2∞). And their direct subgroups [∞,4*]+, [∞*,4]+, subgroup indices 16 and ∞ respectively, can be given in orbifold notation as (∞∞∞∞) and (2∞).
| Small index subgroups of [∞,4], (*∞42) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | 1 | 2 | 4 | ||||||||
| Diagram | 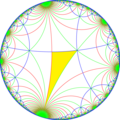
|
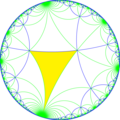
|

|
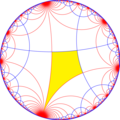
|
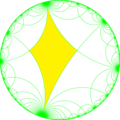
|

| |||||
| Coxeter | [∞,4] |
[1+,∞,4] |
[∞,4,1+] |
[∞,1+,4] |
[1+,∞,4,1+] |
[∞+,4+] | |||||
| Orbifold | *∞42 | *∞44 | *∞∞2 | *∞222 | *∞2∞2 | ∞2× | |||||
| Semidirect subgroups | |||||||||||
| Diagram | 
|

|

|

|
| ||||||
| Coxeter | [∞,4+] |
[∞+,4] |
[(∞,4,2+)] |
[1+,∞,1+,4] = |
[∞,1+,4,1+] = | ||||||
| Orbifold | 4*∞ | ∞*2 | 2*∞2 | ∞*22 | 2*∞∞ | ||||||
| Direct subgroups | |||||||||||
| Index | 2 | 4 | 8 | ||||||||
| Diagram | 
|
|

|
|

| ||||||
| Coxeter | [∞,4]+ |
[∞,4+]+ |
[∞+,4]+ |
[∞,1+,4]+ |
[∞+,4+]+ = [1+,∞,1+,4,1+] | ||||||
| Orbifold | ∞42 | ∞44 | ∞∞2 | ∞222 | ∞2∞2 | ||||||
| Radical subgroups | |||||||||||
| Index | 8 | ∞ | 16 | ∞ | |||||||
| Diagram | 
|
|

|

| |||||||
| Coxeter | [∞,4*] |
[∞*,4] |
[∞,4*]+ |
[∞*,4]+ | |||||||
| Orbifold | *∞∞∞∞ | *2∞ | ∞∞∞∞ | 2∞ | |||||||
See also[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Uniform tiling 4-8-i. |
- Tilings of regular polygons
- List of uniform planar tilings
References[]
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strass, The Symmetries of Things 2008, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 19, The Hyperbolic Archimedean Tessellations)
- "Chapter 10: Regular honeycombs in hyperbolic space". The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays. Dover Publications. 1999. ISBN 0-486-40919-8. LCCN 99035678.
External links[]
- Apeirogonal tilings
- Hyperbolic tilings
- Isogonal tilings
- Semiregular tilings
- Truncated tilings


