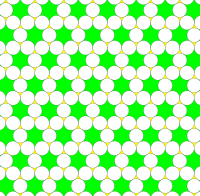
Trihexagonal tiling
| Trihexagonal tiling | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Semiregular tiling |
| Vertex configuration |  (3.6)2 |
| Schläfli symbol | r{6,3} or h2{6,3} |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 | 6 3 3 3 | 3 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry | p6m, [6,3], (*632) |
| Rotation symmetry | p6, [6,3]+, (632) p3, [3[3]]+, (333) |
| Bowers acronym | That |
| Dual | Rhombille tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive Edge-transitive |
In geometry, the trihexagonal tiling is one of 11 uniform tilings of the Euclidean plane by regular polygons.[1] It consists of equilateral triangles and regular hexagons, arranged so that each hexagon is surrounded by triangles and vice versa. The name derives from the fact that it combines a regular hexagonal tiling and a regular triangular tiling. Two hexagons and two triangles alternate around each vertex, and its edges form an infinite arrangement of lines. Its dual is the rhombille tiling.[2]
This pattern, and its place in the classification of uniform tilings, was already known to Johannes Kepler in his 1619 book Harmonices Mundi.[3] The pattern has long been used in Japanese basketry, where it is called kagome. The Japanese term for this pattern has been taken up in physics, where it is called a Kagome lattice. It occurs also in the crystal structures of certain minerals. Conway calls it a hexadeltille, combining alternate elements from a hexagonal tiling (hextille) and triangular tiling (deltille).[4]
Kagome[]

Kagome (Japanese: 籠目) is a traditional Japanese woven bamboo pattern; its name is composed from the words kago, meaning "basket", and me, meaning "eye(s)", referring to the pattern of holes in a woven basket.

It is a woven arrangement of laths composed of interlaced triangles such that each point where two laths cross has four neighboring points, forming the pattern of a trihexagonal tiling. The woven process gives the Kagome a chiral wallpaper group symmetry, p6, (632).
Kagome lattice[]
The term kagome lattice was coined by Japanese physicist Kôdi Husimi, and first appeared in a 1951 paper by his assistant Ichirō Shōji.[5] The kagome lattice in this sense consists of the vertices and edges of the trihexagonal tiling. Despite the name, these crossing points do not form a mathematical lattice.
A related three dimensional structure formed by the vertices and edges of the quarter cubic honeycomb, filling space by regular tetrahedra and truncated tetrahedra, has been called a hyper-kagome lattice.[6] It is represented by the vertices and edges of the quarter cubic honeycomb, filling space by regular tetrahedra and truncated tetrahedra. It contains four sets of parallel planes of points and lines, each plane being a two dimensional kagome lattice. A second expression in three dimensions has parallel layers of two dimensional lattices and is called an orthorhombic-kagome lattice.[6] The trihexagonal prismatic honeycomb represents its edges and vertices.
Some minerals, namely jarosites and herbertsmithite, contain two-dimensional layers or three-dimensional kagome lattice arrangement of atoms in their crystal structure. These minerals display novel physical properties connected with geometrically frustrated magnetism. For instance, the spin arrangement of the magnetic ions in Co3V2O8 rests in a kagome lattice which exhibits fascinating magnetic behavior at low temperatures.[7] Quantum magnets realized on Kagome lattices have been discovered to exhibit many unexpected electronic and magnetic phenomena.[8][9][10][11] It is also proposed that SYK behavior can be observed in two dimensional kagome lattice with impurities.[12]
The term is much in use nowadays in the scientific literature, especially by theorists studying the magnetic properties of a theoretical kagome lattice.
See also: Kagome crests.
Symmetry[]

The trihexagonal tiling has Schläfli symbol of r{6,3}, or Coxeter diagram, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , symbolizing the fact that it is a rectified hexagonal tiling, {6,3}. Its symmetries can be described by the wallpaper group p6mm, (*632),[13] and the tiling can be derived as a Wythoff construction within the reflectional fundamental domains of this group. The trihexagonal tiling is a quasiregular tiling, alternating two types of polygons, with vertex configuration (3.6)2. It is also a uniform tiling, one of eight derived from the regular hexagonal tiling.
, symbolizing the fact that it is a rectified hexagonal tiling, {6,3}. Its symmetries can be described by the wallpaper group p6mm, (*632),[13] and the tiling can be derived as a Wythoff construction within the reflectional fundamental domains of this group. The trihexagonal tiling is a quasiregular tiling, alternating two types of polygons, with vertex configuration (3.6)2. It is also a uniform tiling, one of eight derived from the regular hexagonal tiling.
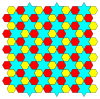
Uniform colorings[]
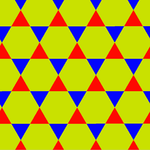
There are two distinct uniform colorings of a trihexagonal tiling. Naming the colors by indices on the 4 faces around a vertex (3.6.3.6): 1212, 1232.[1] The second is called a cantic hexagonal tiling, h2{6,3}, with two colors of triangles, existing in p3m1 (*333) symmetry.
| Symmetry | p6m, (*632) | p3m, (*333) |
|---|---|---|
| Coloring | 
|
|
| fundamental domain |
| |
| Wythoff | 2 | 6 3 | 3 3 | 3 |
| Coxeter | ||
| Schläfli | r{6,3} | r{3[3]} = h2{6,3} |
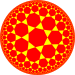
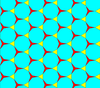
Circle packing[]
The trihexagonal tiling can be used as a circle packing, placing equal diameter circles at the center of every point.[14] Every circle is in contact with 4 other circles in the packing (kissing number).
Topologically equivalent tilings[]
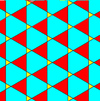
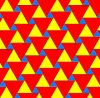
The trihexagonal tiling can be geometrically distorted into topologically equivalent tilings of lower symmetry.[1] In these variants of the tiling, the edges do not necessarily line up to form straight lines.
| p3m1, (*333) | p3, (333) | p31m, (3*3) | cmm, (2*22) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|

|
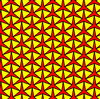
|
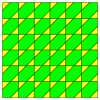
|
Related quasiregular tilings[]
The trihexagonal tiling exists in a sequence of symmetries of quasiregular tilings with vertex configurations (3.n)2, progressing from tilings of the sphere to the Euclidean plane and into the hyperbolic plane. With orbifold notation symmetry of *n32 all of these tilings are wythoff construction within a fundamental domain of symmetry, with generator points at the right angle corner of the domain.[15][16]
| show*n32 orbifold symmetries of quasiregular tilings: (3.n)2 |
|---|
Related regular complex apeirogons[]
There are 2 regular complex apeirogons, sharing the vertices of the trihexagonal tiling. Regular complex apeirogons have vertices and edges, where edges can contain 2 or more vertices. Regular apeirogons p{q}r are constrained by: 1/p + 2/q + 1/r = 1. Edges have p vertices arranged like a regular polygon, and vertex figures are r-gonal.[17]
The first is made of triangular edges, two around every vertex, second has hexagonal edges, two around every vertex.
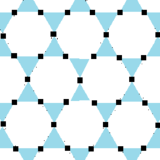
|

|
| 3{12}2 or |
6{6}2 or |
|---|
See also[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Uniform tiling 3-6-3-6. |
- Percolation threshold
- Kagome crest
- Star of David
- Trihexagonal prismatic honeycomb
- Cyclotruncated simplectic honeycomb
- List of uniform tilings
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Grünbaum, Branko; Shephard, G. C. (1987). Tilings and Patterns. W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-1193-3. See in particular Theorem 2.1.3, p. 59 (classification of uniform tilings); Figure 2.1.5, p.63 (illustration of this tiling), Theorem 2.9.1, p. 103 (classification of colored tilings), Figure 2.9.2, p. 105 (illustration of colored tilings), Figure 2.5.3(d), p. 83 (topologically equivalent star tiling), and Exercise 4.1.3, p. 171 (topological equivalence of trihexagonal and two-triangle tilings).
- ^ Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. p. 38. ISBN 0-486-23729-X.
- ^ Aiton, E. J.; Duncan, Alistair Matheson; Field, Judith Veronica, eds. (1997), The Harmony of the World by Johannes Kepler, Memoirs of the American Philosophical Society, 209, American Philosophical Society, pp. 104–105, ISBN 9780871692092.
- ^ Conway, John H.; Burgiel, Heidi; Goodman-Strauss, Chaim (2008). "Chapter 21: Naming Archimedean and Catalan polyhedra and tilings; Euclidean plane tessellations". The Symmetries of Things. Wellesley, MA: A K Peters, Ltd. p. 288. ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5. MR 2410150.
- ^ Mekata, Mamoru (February 2003). "Kagome: The story of the basketweave lattice". Physics Today. 56 (2): 12–13. Bibcode:2003PhT....56b..12M. doi:10.1063/1.1564329.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lawler, Michael J.; Kee, Hae-Young; Kim, Yong Baek; Vishwanath, Ashvin (2008). "Topological spin liquid on the hyperkagome lattice of Na4Ir3O8". Physical Review Letters. 100 (22): 227201. arXiv:0705.0990. Bibcode:2008PhRvL.100v7201L. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.100.227201. PMID 18643453. S2CID 31984687.
- ^ Yen, F., Chaudhury, R. P., Galstyan, E., Lorenz, B., Wang, Y. Q., Sun, Y. Y., Chu, C. W. (2008). "Magnetic phase diagrams of the Kagome staircase compound Co3V2O8". Physica B: Condensed Matter. 403 (5–9): 1487–1489. arXiv:0710.1009. Bibcode:2008PhyB..403.1487Y. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2007.10.334. S2CID 14958188.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^ "A quantum magnet with a topological twist". Discovery: Research at Princeton. 2019-02-22. Retrieved 2020-04-26.
- ^ Yin, Jia-Xin; Zhang, Songtian S.; Li, Hang; Jiang, Kun; Chang, Guoqing; Zhang, Bingjing; Lian, Biao; Xiang, Cheng; Belopolski (2018). "Giant and anisotropic many-body spin–orbit tunability in a strongly correlated kagome magnet". Nature. 562 (7725): 91–95. arXiv:1810.00218. Bibcode:2018Natur.562...91Y. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0502-7. PMID 30209398. S2CID 205570556.
- ^ Yin, Jia-Xin; Zhang, Songtian S.; Chang, Guoqing; Wang, Qi; Tsirkin, Stepan S.; Guguchia, Zurab; Lian, Biao; Zhou, Huibin; Jiang, Kun; Belopolski, Ilya; Shumiya, Nana (2019). "Negative flat band magnetism in a spin–orbit-coupled correlated kagome magnet". Nature Physics. 15 (5): 443–8. arXiv:1901.04822. Bibcode:2019NatPh..15..443Y. doi:10.1038/s41567-019-0426-7. S2CID 119363372.
- ^ Yazyev, Oleg V. (2019). "An upside-down magnet". Nature Physics. 15 (5): 424–5. Bibcode:2019NatPh..15..424Y. doi:10.1038/s41567-019-0451-6. S2CID 128299874.
- ^ Wei, Chenan; Sedrakyan, Tigran (2021-01-29). "Optical lattice platform for the Sachdev-Ye-Kitaev model". Phys. Rev. A. 103 (1): 013323. arXiv:2005.07640. Bibcode:2021PhRvA.103a3323W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.103.013323.
- ^ Steurer, Walter; Deloudi, Sofia (2009). Crystallography of Quasicrystals: Concepts, Methods and Structures. Springer Series in Materials Science. 126. Springer. p. 20. ISBN 9783642018992.
- ^ Critchlow, Keith (2000) [1969]. "pattern G". Order in Space: A design source book. Thames & Hudson. pp. 74–75. ISBN 9780500340332.
- ^ Coxeter, H.S.M. (1973). "V. The Kaleidoscope, §5.7 Wythoff's construction". Regular Polytopes (3rd ed.). Dover. ISBN 0-486-61480-8.
- ^ Huson, Daniel H. "Two Dimensional symmetry Mutations". CiteSeerX 10.1.1.30.8536. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ Coxeter, H.S.M. (1991). Regular Complex Polytopes (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 111–2, 136. ISBN 9780521394901.
Further reading[]
- Seymour, Dale; Britton, Jill (1989). Introduction to Tessellations. pp. 50–56. ISBN 978-0866514613.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kagome structures. |
- Euclidean tilings
- Isogonal tilings
- Isotoxal tilings
- Semiregular tilings
- Quasiregular polyhedra
- Japanese bamboowork
- Crystallography