Chlorine monofluoride
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chlorine monofluoride
| |
| Other names
Chlorine fluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.300 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
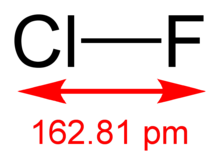
Chemical formula
|
ClF |
| Molar mass | 54.45 g/mol |
| Density | 1.62 g mL (liquid, −100 °C) |
| Melting point | −155.6 °C (−248.1 °F; 117.5 K) |
| Boiling point | −100.1 °C (−148.2 °F; 173.1 K) |
| Structure | |
Dipole moment
|
0.881 D (2.94 × 10−30 C m) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
33.01 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S |
217.91 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−56.5 kJ mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chlorine monofluoride is a volatile interhalogen compound with the chemical formula ClF. It is a colourless gas at room temperature and is stable even at high temperatures. When cooled to −100 °C, ClF condenses as a pale yellow liquid. Many of its properties are intermediate between its parent halogens, Cl2 and F2.[1]
Reactivity[]
Chlorine monofluoride is a versatile fluorinating agent, converting metals and non-metals to their fluorides and releasing Cl2 in the process. For example, it converts tungsten to tungsten hexafluoride and selenium to selenium tetrafluoride:
- W + 6 ClF → WF6 + 3 Cl2
- Se + 4 ClF → SeF4 + 2 Cl2
FCl can also chlorofluorinate compounds, either by addition across a multiple bond or via oxidation. For example, it adds fluorine and chlorine to the carbon of carbon monoxide, yielding carbonyl chloride fluoride:
- CO + ClF →

See also[]
References[]
- ^ Otto Ruff, E. Ascher (1928). "Über ein neues Chlorfluorid-CIF3". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 176 (1): 258–270. doi:10.1002/zaac.19281760121.
External links[]
- Fluorides
- Fluorinating agents
- Inorganic chlorine compounds
- Interhalogen compounds
- Oxidizing agents