Fluorobenzene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Fluorobenzene | |||
| Other names
Phenyl fluoride
Monofluorobenzene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1236623 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.657 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 49856 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2387 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula
|
C6H5F | ||
| Molar mass | 96.103 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.025 g/mL, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −44 °C (−47 °F; 229 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 84 to 85 °C (183 to 185 °F; 357 to 358 K) | ||
| low | |||
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
|
-58.4·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Structure | |||
| Planar | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
Signal word
|
Warning | ||
| H225, H318, H411 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P273, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P310, P337+P313, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 
1
3
0 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related halobenzenes
|
Chlorobenzene Bromobenzene Iodobenzene | ||
Related compounds
|
Benzene 1,2-Difluorobenzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Fluorobenzene is the chemical compound with the formula C6H5F, often abbreviated PhF. A colorless liquid, it is a precursor to many fluorophenyl compounds.
Preparation[]
PhF was first reported in 1886 by O. Wallach at the University of Bonn, who prepared the compound in two steps. Phenyldiazonium chloride was first converted to a triazene using piperidine:
- [PhN2]Cl + 2 (CH2)5NH → PhN=N-N(CH2)5 + [(CH2)5NH2]Cl
The triazine was then cleaved with hydrofluoric acid:
- PhN=N-N(CH2)5 + 2 HF → PhF + N2 + [(CH2)5NH2]F
Historical note: in Wallach's era, the element fluorine was symbolized with "Fl". Thus, his procedure is subtitled "Fluorbenzol, C6H5Fl".[1]
On the laboratory scale, PhF is prepared by the thermal decomposition of the benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate:
- PhN2BF4 → PhF + BF3 + N2
According to the procedure, solid [PhN2]BF4 is heated with a flame to initiate an exothermic reaction, which also affords boron trifluoride and nitrogen gas. Product PhF and BF3 are readily separated because of their differing boiling points.[2]
The technical synthesis is by the reaction of cyclopentadiene with difluorocarbene. The initially formed cyclopropane undergoes a ring expansion and subsequent elimination of hydrogen fluoride.
Reactions[]
PhF behaves rather differently from other halobenzene derivatives owing to the pi-donor properties of fluoride. For example, the para position is more activated than benzene toward electrophiles. For this reason, it can be converted to 1-bromo-4-fluorobenzene with relatively high efficiency.[3]
Solvent properties[]
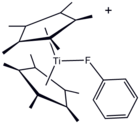 Structure of [(C5Me5)2Ti(FC6H5)]+, a coordination complex of fluorobenzene.
Structure of [(C5Me5)2Ti(FC6H5)]+, a coordination complex of fluorobenzene.
PhF is a useful solvent for highly reactive species. Its melting point at -44 °C is lower than that of benzene. In contrast, the boiling points of PhF and benzene are very similar, differing by only 4 °C. It is considerably more polar than benzene, with a dielectric constant of 5.42 compared to 2.28 for benzene at 298 K.[4] Fluorobenzene is a relatively inert compound reflecting the strength of the C–F bond.
Although it is usually considered a non-coordinating solvent, a metal complex of PhF has been crystallized.[5]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Wallach, O. "Über einen Weg zur leichten Gewinnung organischer Fluorverbindungen" (Concerning a method for easily preparing organic fluorine compounds) Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie, 1886, Volume 235, p. 255–271; doi:10.1002/jlac.18862350303
- ^ Flood, D. T. (1933). "Fluorobenzene". Org. Synth. 13: 46. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.013.0046..
- ^ Rosenthal, Joel; Schuster, David I. (2003). "The Anomalous Reactivity of Fluorobenzene in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and Related Phenomena". J. Chem. Educ. 80 (6): 679. Bibcode:2003JChEd..80..679R. doi:10.1021/ed080p679.
- ^ Table of Dielectric Constants of Pure Liquids. National Bureau of Standards. 1951.
- ^ R.N. Perutz and T. Braun "Transition Metal-mediated C–F Bond Activation" Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry III, 2007, Volume 1, p. 725–758; doi:10.1016/B0-08-045047-4/00028-5.
- Fluoroarenes
- Phenyl compounds