Gallopamil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Methoxyverapamil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
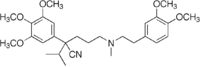
| Formula | C28H40N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 484.637 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Gallopamil (INN) is an L-type calcium channel blocker that is an analog of verapamil. It is used in the treatment of abnormal heart rhythms.[1]
References[]
- ^ Sewing KF, Hannemann H (1983). "Calcium channel antagonists verapamil and gallopamil are powerful inhibitors of acid secretion in isolated and enriched guinea pig parietal cells". Pharmacology. 27 (1): 9–14. doi:10.1159/000137824. PMID 6310646.
Categories:
- Calcium channel blockers
- Pyrogallol ethers
- Nitriles
- Phenethylamines
- Isopropyl compounds
- Cardiovascular system drug stubs