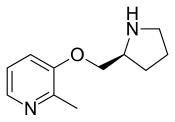
Pozanicline
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H16N2O |
| Molar mass | 192.258 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Pozanicline (INN,[1] codenamed ABT-089) is a drug developed by Abbott, that has nootropic and neuroprotective effects.[2][3][4] Animal studies suggested it useful for the treatment of ADHD[5] and subsequent human trials have shown ABT-089 to be effective for this application.[6] It binds with high affinity subtype-selective to the α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and has partial agonism to the subtype,[7][8] but not the α7 and α3β4 subtypes familiar to nicotine. It has particularly low tendency to cause side effects compared to other drugs in the class,[9][10] making it an exciting candidate for clinical development.
Synthesis[]
Pozanicline is synthesized from 2-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine and Boc-L-Prolinol through a dehydration reaction followed by deprotection of the nitrogen atom of prolinol[11]
References[]
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 62" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 257. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 May 2016. Retrieved 3 January 2017.
- ^ Lin NH, Gunn DE, Ryther KB, Garvey DS, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Decker MW, et al. (January 1997). "Structure-activity studies on 2-methyl-3-(2(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy) pyridine (ABT-089): an orally bioavailable 3-pyridyl ether nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand with cognition-enhancing properties". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 40 (3): 385–90. doi:10.1021/jm960233u. PMID 9022806.
- ^ Sullivan JP, Donnelly-Roberts D, Briggs CA, Anderson DJ, Gopalakrishnan M, Xue IC, et al. (October 1997). "ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine]: I. A potent and selective cholinergic channel modulator with neuroprotective properties". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 283 (1): 235–46. PMID 9336329.
- ^ Decker MW, Bannon AW, Curzon P, Gunther KL, Brioni JD, Holladay MW, et al. (October 1997). "ABT-089 [2-methyl-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine dihydrochloride]: II. A novel cholinergic channel modulator with effects on cognitive performance in rats and monkeys". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 283 (1): 247–58. PMID 9336330.
- ^ Prendergast MA, Jackson WJ, Terry AV, Decker MW, Arneric SP, Buccafusco JJ (March 1998). "Central nicotinic receptor agonists ABT-418, ABT-089, and (-)-nicotine reduce distractibility in adult monkeys". Psychopharmacology. 136 (1): 50–8. doi:10.1007/s002130050538. PMID 9537682. S2CID 20080069.
- ^ Wilens TE, Verlinden MH, Adler LA, Wozniak PJ, West SA (June 2006). "ABT-089, a neuronal nicotinic receptor partial agonist, for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults: results of a pilot study". Biological Psychiatry. 59 (11): 1065–70. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.10.029. PMID 16499880. S2CID 24951969.
- ^ Marks MJ, Wageman CR, Grady SR, Gopalakrishnan M, Briggs CA (October 2009). "Selectivity of ABT-089 for alpha4beta2* and alpha6beta2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in brain". Biochemical Pharmacology. 78 (7): 795–802. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.05.022. PMC 2772152. PMID 19481067.
- ^ Anderson DJ, Malysz J, Grønlien JH, El Kouhen R, Håkerud M, Wetterstrand C, et al. (October 2009). "Stimulation of dopamine release by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands in rat brain slices correlates with the profile of high, but not low, sensitivity alpha4beta2 subunit combination". Biochemical Pharmacology. 78 (7): 844–51. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.024. PMID 19555668.
- ^ Rueter LE, Anderson DJ, Briggs CA, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Gintant GA, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. (2004). "ABT-089: pharmacological properties of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the potential treatment of cognitive disorders". CNS Drug Reviews. 10 (2): 167–82. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00011.x. PMC 6741767. PMID 15179445.
- ^ Wilens TE, Decker MW (October 2007). "Neuronal nicotinic receptor agonists for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: focus on cognition". Biochemical Pharmacology. 74 (8): 1212–23. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.07.002. PMC 2974320. PMID 17689498.
- ^ Rueter LE, Anderson DJ, Briggs CA, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Gintant GA, Gopalakrishnan M, et al. (2006). "ABT-089: pharmacological properties of a neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for the potential treatment of cognitive disorders". CNS Drug Reviews. 10 (2): 167–82. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2004.tb00011.x. PMC 6741767. PMID 15179445.
- Nicotinic agonists
- Nootropics
- Phenol ethers
- Pyridines
- Pyrrolidines
- Stimulants