Solriamfetol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sunosi |
| Other names | SKL-N05, ADX-N05, ARL-N05, YKP10A, R228060, and JZP-110; (R)-2-amino-3-phenylpropylcarbamate hydrochloride |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a619040 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~95%[1] |
| Protein binding | 13.3–19.4%[1] |
| Metabolism | Minimal[1] |
| Elimination half-life | ~7.1 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (95% unchanged) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 194.234 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
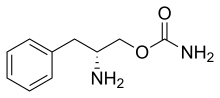
Solriamfetol, sold under the brand name Sunosi, is a medication used for the treatment of excessive sleepiness associated with narcolepsy and sleep apnea.[1] It is derived from d-phenylalanine and its chemical name is (R)-2-amino-3-phenylpropylcarbamate hydrochloride.[3] It is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI). Common side effects include headache, nausea, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.[1]
The drug was discovered by a subsidiary of SK Group, which licensed rights outside of eleven countries in Asia to Aerial Pharma in 2011.[4]
Pharmacology[]
Pharmacodynamics[]
Solriamfetol is a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI).[1] It binds to the dopamine transporter and the norepinephrine transporter with affinities (Ki) of 14.2 μM and 3.7 μM, respectively).[1] It inhibits the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine with IC50 values of 2.9 μM and 4.4 μM, respectively.[1] It has weak affinity for the serotonin transporter (Ki = 81.5 μM) and does not appreciably inhibit serotonin reuptake (IC50 > 100 μM).[1] Solriamfetol has no appreciable affinity for a variety of other targets, including the dopamine, serotonin, adrenergic, GABA, adenosine, histamine, orexin, benzodiazepine, and acetylcholine receptors.[1]
Pharmacokinetics[]
The elimination half-life of solriamfetol is about 7.1 hours.[1]
History[]
The drug was discovered by a subsidiary of SK Group, which licensed rights outside of eleven countries in Asia to Aerial Pharma in 2011.[4] Aerial ran two Phase II trials of the drug in narcolepsy[5] before selling the license to solriamfetol to Jazz in 2014; Jazz Pharmaceuticals paid Aerial $125 million up front and will pay Aerial and SK up to $272 million in milestone payments, and will pay double-digit royalties to SK.[4][6]
In 2019, solriamfetol was approved in the United States to improve wakefulness in adults with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).[7][8] It was granted orphan drug designation.[9]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved solriamfetol based primarily on evidence from five clinical trials (Trial 1/NCT02348593, Trial 2/NCT02348606, Trial 3/NCT02348619, Trial 4/NCT02348632, Trial 5 NCT01681121) of 622 patients with narcolepsy or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).[7] The trials were conducted in Canada, Europe, and the United States.[7]
Solriamfetol was approved for medical use in the European Union in January 2020.[2]
Society and culture[]
Names[]
During development it has been called SKL-N05, ADX-N05, ARL-N05, and JZP-110.[10]
Legal status[]
In the United States, solriamfetol is a Schedule IV controlled substance,[1] meaning that it has an accepted medical use and a low potential for abuse, but that abuse may lead to physical or psychological dependence.[11] A prescription is required, and can only be refilled up to five times in a six-month period.[12] In countries of the European Union, a prescription is required.[2]
Research[]
This section needs expansion. You can help by . (October 2021) |
A case report of solriamfetol for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) exists.[13]
References[]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "Sunosi – solriamfetol tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 16 October 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ a b c "Sunosi EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 12 November 2019. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- ^ Abad VC, Guilleminault C (2017). "New developments in the management of narcolepsy". Nature and Science of Sleep. 9: 39–57. doi:10.2147/NSS.S103467. PMC 5344488. PMID 28424564.
- ^ a b c Ji-young S (5 March 2018). "SK Biopharmaceuticals' narcolepsy drug on track to hitting US market". The Korea Herald.
- ^ Sullivan SS, Guilleminault C (2015). "Emerging drugs for common conditions of sleepiness: obstructive sleep apnea and narcolepsy". Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs. 20 (4): 571–82. doi:10.1517/14728214.2015.1115480. PMID 26558298. S2CID 7951307.
- ^ Garde D (14 January 2014). "Jazz bets up to $397M on Aerial's narcolepsy drug". FierceBiotech.
- ^ a b c "Drug Trials Snapshots: Sunosi". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 16 April 2019. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Sunosi". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 April 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Solriamfetol Orphan Drug Approval". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 24 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Solriamfetol – Jazz Pharmaceuticals/SK Biopharmaceuticals". AdisInsight. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ^ 21 U.S.C. § 812 – Schedules of controlled substances
- ^ "Manuals – Practitioner's Manual – Section V". Retrieved 2014-01-07
- ^ Naguy A, El-Sheshaie A, Elsori DH, Alamiri B (April 2021). "Solriamfetol for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder". CNS Spectr: 1–2. doi:10.1017/S1092852921000328. PMID 33870884.
External links[]
- "Solriamfetol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- * "Solriamfetol hydrochloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Carbamates
- Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors
- Orphan drugs
- Phenethylamines
- Stimulants