This article
does not cite any sources .
Please help by adding citations to reliable sources . Unsourced material may be challenged and removed .Find sources: – · · · scholar · JSTOR (November 2014 ) (Learn how and when to remove this template message
Etanautine ATC code
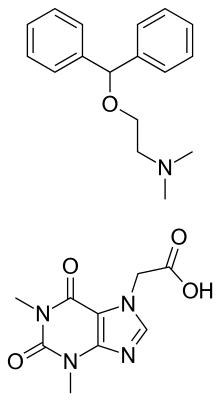
2-[di(phenyl)methoxy]-N,N-dimethylethanamine; 2-(1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxopurin-7-yl)acetic acid
CAS Number ChemSpider UNII Formula C 26 H 31 N 5 O 5 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
O=C2N(c1ncn(c1C(=O)N2C)CC(=O)O)C.O(CCN(C)C)C(c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2
InChI=1S/C17H21NO.C9H10N4O4/c1-18(2)13-14-19-17(15-9-5-3-6-10-15)16-11-7-4-8-12-16;1-11-7-6(8(16)12(2)9(11)17)13(4-10-7)3-5(14)15/h3-12,17H,13-14H2,1-2H3;4H,3H2,1-2H3,(H,14,15)
Key:UFKLOBYBVCBTBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Etanautine , also known as diphenhydramine monoacefyllinate , is an anticholinergic used as an antiparkinsonian agent. It is a 1:1 salt of diphenhydramine with acefylline , similar to the diphenhydramine/8-chlorotheophylline combination product dimenhydrinate .
As with dimenhydrinate, the stimulant effect of the etanautine counteracts the sedative effect from the diphenhydramine, resulting in an improved therapeutic profile.
The 1:2 salt diphenhydramine diacefylline (with two molecules of acefylline to each molecule of diphenhydramine) is also used in medicine, under the brand name Nautamine .
References [ ]
Dopaminergics
DA precursors DA receptor agonists
Ergoline: Bromocriptine Cabergoline Dihydroergocryptine Lisuride Pergolide Non-ergoline: Apomorphine Piribedil Pramipexole Ropinirole Rotigotine Talipexole MAO-B inhibitors
Rasagiline Safinamide Selegiline COMT inhibitors
Entacapone Opicapone Tolcapone AAAD inhibitors
Anticholinergics Others
Amantadine Budipine Istradefylline Methylxanthines (e.g., caffeine )Rimantadine
# WHO-EM ‡ Withdrawn from marketClinical trials :
† Phase III § Never to phase III
Stimulants
Adamantanes
Adapromine Amantadine Bromantane Memantine Rimantadine Adenosine antagonists Alkylamines
Cyclopentamine Cypenamine Cyprodenate Heptaminol Isometheptene Levopropylhexedrine Methylhexaneamine Octodrine Propylhexedrine Tuaminoheptane Ampakines Arylcyclohexylamines Benzazepines
6-Br-APB SKF-77434 SKF-81297 SKF-82958 Cathinones Cholinergics Convulsants Eugeroics Oxazolines
4-Methylaminorex Aminorex Clominorex Cyclazodone Fenozolone Fluminorex Pemoline Thozalinone Phenethylamines Phenylmorpholines Piperazines
2C-B-BZP 3C-PEP BZP CM156 DBL-583 GBR-12783 GBR-12935 GBR-13069 GBR-13098 GBR-13119 MeOPP MBZP oMPP Vanoxerine Piperidines
1-Benzyl-4-(2-(diphenylmethoxy)ethyl)piperidine 2-Benzylpiperidine 2-Methyl-3-phenylpiperidine 3,4-Dichloromethylphenidate 4-Benzylpiperidine 4-Fluoromethylphenidate 4-Methylmethylphenidate Desoxypipradrol Difemetorex Diphenylpyraline Ethylnaphthidate Ethylphenidate Methylnaphthidate Isopropylphenidate JZ-IV-10 Methylphenidate (Dexmethylphenidate )Nocaine Phacetoperane Pipradrol Propylphenidate SCH-5472 Pyrrolidines Racetams
Oxiracetam Phenylpiracetam Phenylpiracetam hydrazide Tropanes
4-fluorotropacocaine 4'-Fluorococaine Altropane (IACFT) Brasofensine CFT (WIN 35,428) β-CIT (RTI-55) Cocaethylene Cocaine Dichloropane (RTI-111) Difluoropine FE-β-CPPIT FP-β-CPPIT Ioflupane (123 I) Norcocaine PIT PTT RTI-31 RTI-32 RTI-51 RTI-112 RTI-113 RTI-120 RTI-121 (IPCIT) RTI-126 RTI-150 RTI-177 RTI-229 RTI-336 RTI-354 RTI-371 RTI-386 Salicylmethylecgonine Tesofensine Troparil (β-CPT, WIN 35,065-2) Tropoxane WF-23 WF-33 Tryptamines Others ATC code : N06B
mAChRs
Agonists Antagonists
3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate 4-DAMP Aclidinium bromide (+formoterol )Abediterol AF-DX 384 Ambutonium bromide Anisodamine Anisodine Antihistamines (first-generation) (e.g., brompheniramine , buclizine , captodiame , chlorphenamine (chlorpheniramine) , cinnarizine , clemastine , cyproheptadine , dimenhydrinate , dimetindene , diphenhydramine , doxylamine , meclizine , mequitazine , perlapine , phenindamine , pheniramine , phenyltoloxamine , promethazine , propiomazine , triprolidine )Atropine Atropine methonitrate Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine , fluperlapine , olanzapine (+fluoxetine ), , quetiapine , tenilapine , zotepine )Benactyzine Benzatropine (benztropine) Benzilone Benzilylcholine mustard Benzydamine Biperiden Bornaprine Camylofin CAR-226,086 CAR-301,060 CAR-302,196 CAR-302,282 CAR-302,668 Caramiphen Cimetropium bromide Clidinium bromide Cloperastine CS-27349 Cyclobenzaprine Cyclopentolate Darifenacin Desfesoterodine Dexetimide Dicycloverine (dicyclomine) Dihexyverine Difemerine Diphemanil metilsulfate Ditran Drofenine EA-3167 EA-3443 EA-3580 EA-3834 Emepronium bromide Etanautine Etybenzatropine (ethybenztropine) Fenpiverinium Fentonium bromide Fesoterodine Flavoxate Glycopyrronium bromide (+beclometasone/formoterol , +indacaterol )Hexocyclium Himbacine Homatropine Imidafenacin Ipratropium bromide (+salbutamol )Isopropamide Hyoscyamine Mamba toxin 3 Mamba toxin 7 Mazaticol Mebeverine Meladrazine Mepenzolate Methantheline Methoctramine Methylatropine Methylhomatropine Methylscopolamine Metixene Muscarinic toxin 7 N-Ethyl-3-piperidyl benzilate N-Methyl-3-piperidyl benzilate Nefopam Octatropine methylbromide (anisotropine methylbromide) Orphenadrine Otenzepad (AF-DX 116) Otilonium bromide Oxapium iodide Oxitropium bromide Oxybutynin Oxyphencyclimine Oxyphenonium bromide PD-102,807 PD-0298029 Penthienate Pethidine Phenglutarimide Phenyltoloxamine Pipenzolate bromide Piperidolate Pirenzepine Piroheptine Pizotifen Poldine Pridinol Prifinium bromide Procyclidine Profenamine (ethopropazine) Propantheline bromide Propiverine Quinidine 3-Quinuclidinyl thiochromane-4-carboxylate Revefenacin Rociverine Scopolamine (hyoscine) Scopolamine butylbromide (hyoscine butylbromide) Sofpironium bromide Solifenacin SSRIs femoxetine , paroxetine )Telenzepine Terodiline Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine , maprotiline , mianserin , mirtazapine )Tiemonium iodide Timepidium bromide Tiotropium bromide Tofenacin Tolterodine Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline (+perphenazine ), amitriptylinoxide , butriptyline , cidoxepin , clomipramine , desipramine , , dibenzepin , dosulepin (dothiepin) , doxepin , imipramine , lofepramine , nitroxazepine , northiaden (desmethyldosulepin) , nortriptyline , protriptyline , quinupramine , trimipramine )Tridihexethyl Trihexyphenidyl Trimebutine Tropatepine Tropicamide Trospium chloride Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , chlorprothixene , cyamemazine (cyamepromazine) , loxapine , mesoridazine , thioridazine )Umeclidinium bromide (+vilanterol )WIN-2299 Xanomeline
Precursors (and prodrugs )
Acetyl-coA Adafenoxate Choline (lecithin )Citicoline Cyprodenate Dimethylethanolamine Glycerophosphocholine Meclofenoxate (centrophenoxine) Phosphatidylcholine Phosphatidylethanolamine Phosphorylcholine Pirisudanol See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators • Acetylcholine metabolism/transport modulators