From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article
needs additional citations for verification .
Please help by adding citations to reliable sources . Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: – · · · scholar · JSTOR (October 2021 ) (Learn how and when to remove this template message
Homatropine AHFS /Drugs.com Monograph MedlinePlus a601006 ATC code Legal status
Rx only, not FDA approved, only sold in UK
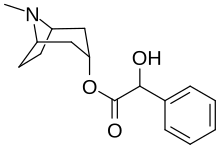
(N -Methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl) 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate
CAS Number PubChem CID DrugBank ChemSpider UNII ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) ECHA InfoCard 100.001.561 Formula C 16 H 21 N O 3 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
CN3[C@H]1CC[C@@H]3C[C@@H](C1)OC(=O)C(O)c2ccccc2
InChI=1S/C16H21NO3/c1-17-12-7-8-13(17)10-14(9-12)20-16(19)15(18)11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-6,12-15,18H,7-10H2,1H3/t12-,13+,14+,15?
Y Key:ZTVIKZXZYLEVOL-MCOXGKPRSA-N
Y N Y (what is this?)
Homatropine (Equipin, Isopto Homatropine) is an anticholinergic medication that is an antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and thus the parasympathetic nervous system . It is used in eye drops as a cycloplegic (to temporarily paralyze accommodation ), and as a mydriatic (to dilate the pupil ).
The related chemical compound homatropine methylbromide (methylhomatropine) is a different medication. Homatropine is less potent than atropine and has a shorter duration of action. It is available as the hydrobromide salt . Homatropine is also given as an atropine substitute given to reverse the muscarinic and CNS effects associated with indirect cholinomimetic (anti-AChase) administration.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines .[1]
Side effects [ ] Contraindications [ ] Untreated glaucoma
Myasthenia gravis Severe heart failure
Thyrotoxicosis References [ ]
^ World Health Organization (2021). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 22nd list (2021) . Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl :10665/345533
Anticholinergics /antimuscarinics Sympathomimetics
mAChRs
Agonists Antagonists
3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate 4-DAMP Aclidinium bromide (+formoterol )Abediterol AF-DX 384 Ambutonium bromide Anisodamine Anisodine Antihistamines (first-generation) (e.g., brompheniramine , buclizine , captodiame , chlorphenamine (chlorpheniramine) , cinnarizine , clemastine , cyproheptadine , dimenhydrinate , dimetindene , diphenhydramine , doxylamine , meclizine , mequitazine , perlapine , phenindamine , pheniramine , phenyltoloxamine , promethazine , propiomazine , triprolidine )Atropine Atropine methonitrate Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine , fluperlapine , olanzapine (+fluoxetine ), , quetiapine , tenilapine , zotepine )Benactyzine Benzatropine (benztropine) Benzilone Benzilylcholine mustard Benzydamine Biperiden Bornaprine Camylofin CAR-226,086 CAR-301,060 CAR-302,196 CAR-302,282 CAR-302,668 Caramiphen Cimetropium bromide Clidinium bromide Cloperastine CS-27349 Cyclobenzaprine Cyclopentolate Darifenacin Desfesoterodine Dexetimide Dicycloverine (dicyclomine) Dihexyverine Difemerine Diphemanil metilsulfate Ditran Drofenine EA-3167 EA-3443 EA-3580 EA-3834 Emepronium bromide Etanautine Etybenzatropine (ethybenztropine) Fenpiverinium Fentonium bromide Fesoterodine Flavoxate Glycopyrronium bromide (+beclometasone/formoterol , +indacaterol )Hexocyclium Himbacine Homatropine Imidafenacin Ipratropium bromide (+salbutamol )Isopropamide Hyoscyamine Mamba toxin 3 Mamba toxin 7 Mazaticol Mebeverine Meladrazine Mepenzolate Methantheline Methoctramine Methylatropine Methylhomatropine Methylscopolamine Metixene Muscarinic toxin 7 N-Ethyl-3-piperidyl benzilate N-Methyl-3-piperidyl benzilate Nefopam Octatropine methylbromide (anisotropine methylbromide) Orphenadrine Otenzepad (AF-DX 116) Otilonium bromide Oxapium iodide Oxitropium bromide Oxybutynin Oxyphencyclimine Oxyphenonium bromide PD-102,807 PD-0298029 Penthienate Pethidine Phenglutarimide Phenyltoloxamine Pipenzolate bromide Piperidolate Pirenzepine Piroheptine Pizotifen Poldine Pridinol Prifinium bromide Procyclidine Profenamine (ethopropazine) Propantheline bromide Propiverine Quinidine 3-Quinuclidinyl thiochromane-4-carboxylate Revefenacin Rociverine Scopolamine (hyoscine) Scopolamine butylbromide (hyoscine butylbromide) Sofpironium bromide Solifenacin SSRIs femoxetine , paroxetine )Telenzepine Terodiline Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine , maprotiline , mianserin , mirtazapine )Tiemonium iodide Timepidium bromide Tiotropium bromide Tofenacin Tolterodine Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline (+perphenazine ), amitriptylinoxide , butriptyline , cidoxepin , clomipramine , desipramine , , dibenzepin , dosulepin (dothiepin) , doxepin , imipramine , lofepramine , nitroxazepine , northiaden (desmethyldosulepin) , nortriptyline , protriptyline , quinupramine , trimipramine )Tridihexethyl Trihexyphenidyl Trimebutine Tropatepine Tropicamide Trospium chloride Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine , chlorprothixene , cyamemazine (cyamepromazine) , loxapine , mesoridazine , thioridazine )Umeclidinium bromide (+vilanterol )WIN-2299 Xanomeline
Precursors (and prodrugs ) See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators • Acetylcholine metabolism/transport modulators
Categories :
Muscarinic antagonists Tropanes Pfizer brands Gastrointestinal system drug stubs Hidden categories:
Articles needing additional references from October 2021 All articles needing additional references Drugs with non-standard legal status Articles with changed CASNo identifier Articles with changed DrugBank identifier Articles with changed EBI identifier ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata Articles without KEGG source Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields All stub articles