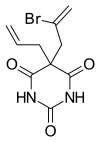
Brallobarbital Other names Brallobarbital ATC code show 3,5 Bromo,4 Acitamido,2 Hydroxy Benzoic Acid Methyl Ester
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider UNII ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) ECHA InfoCard 100.008.387 Formula C 10 H 11 Br N 2 O 3 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol ) show O=C1NC(=O)NC(=O)C1(CC(\Br)=C)C\C=C
show InChI=1S/C10H11BrN2O3/c1-3-4-10(5-6(2)11)7(14)12-9(16)13-8(10)15/h3H,1-2,4-5H2,(H2,12,13,14,15,16)
Y Key:DYODAJAEQDVYFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Y N Y (what is this?)
Brallobarbital was a barbiturate developed in the 1920s.[1] sedative and hypnotic properties, and was used for the treatment of insomnia . Brallobarbital was primarily sold as part of a combination product called Vesparax, composed of 150 mg secobarbital , 50 mg brallobarbital and 50 mg hydroxyzine .[2] [3] [4]
References [ ] show Hypnotics /sedatives (N05C )
GABAA
Alcohols Barbiturates Benzodiazepines
Brotizolam Cinolazepam Climazolam Clonazepam Doxefazepam Estazolam Flunitrazepam Flurazepam Flutoprazepam Lorazepam Loprazolam Lormetazepam Midazolam Nimetazepam Nitrazepam Phenazepam Quazepam Temazepam Triazolam Carbamates Imidazoles Monoureides Neuroactive steroids Nonbenzodiazepines Phenols Piperidinediones Quinazolinones Others
GABAB
1,4-Butanediol 4-Fluorophenibut Aceburic acid Baclofen GABOB GHB (sodium oxybate )GBL GVL Phenibut Tolibut H1
Antihistamines
Captodiame Cyproheptadine Diphenhydramine Doxylamine Hydroxyzine Methapyrilene Perlapine Pheniramine Promethazine Propiomazine Antidepressants
Serotonin antagonists and reuptake inhibitors
Etoperidone Nefazodone Trazodone Tricyclic antidepressants
Amitriptyline Doxepin Trimipramine , etc.Tetracyclic antidepressants
Antipsychotics
Typical antipsychotics
Chlorpromazine Thioridazine , etc.Atypical antipsychotics
α2 -Adrenergic
Clonidine Detomidine Dexmedetomidine Lofexidine Medetomidine Romifidine Tizanidine Xylazine 5-HT2A
Antidepressants
Trazodone Tricyclic antidepressants
Amitriptyline Doxepin Trimipramine , etc.Tetracyclic antidepressants
Antipsychotics
Typical antipsychotics
Chlorpromazine Thioridazine , etc.Atypical antipsychotics
Others
Melatonin Orexin α2 δ VDCC
Gabapentin Gabapentin enacarbil Mirogabalin Phenibut Pregabalin Others
Cannabidiol
Diethylpropanediol Evoxine Fenadiazole Guaifenesin -related muscle relaxants
Chlorphenesin Mephenesin Mephenoxalone Metaxalone Methocarbamol Midaflur Opioids (e.g., morphine )Passion flower Scopolamine Trazodone UMB68 Valnoctamide
show GABA A receptor positive modulatorsAlcohols
Butanol Chloralodol Chlorobutanol (cloretone) Ethanol (alcohol) (alcoholic drink )Ethchlorvynol Isobutanol Isopropanol Menthol Methanol Methylpentynol Pentanol Petrichloral Propanol tert -Butanol (2M2P)tert -Pentanol (2M2B)Tribromoethanol Trichloroethanol Triclofos Trifluoroethanol Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Carbamates Flavonoids
Ampelopsin (dihydromyricetin) Apigenin Baicalein Baicalin Catechin EGC EGCG Hispidulin Luteolin Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin )Wogonin Imidazoles Kava constituents
Desmethoxyyangonin Kavain Methysticin Yangonin Monoureides Neuroactive steroids Nonbenzodiazepines Phenols
Fospropofol Propofol Thymol Piperidinediones Pyrazolopyridines Quinazolinones Volatiles /gases
Acetone Acetophenone Acetylglycinamide chloral hydrate Aliflurane Benzene Butane Butylene Centalun Chloral Chloral betaine Chloral hydrate Chloroform Cryofluorane Desflurane Dichloralphenazone Dichloromethane Diethyl ether Enflurane Ethyl chloride Ethylene Fluroxene Gasoline Halopropane Halothane Isoflurane Kerosine Methoxyflurane Methoxypropane Nitric oxide Nitrogen Nitrous oxide Norflurane Paraldehyde Propane Propylene Roflurane Sevoflurane Synthane Teflurane Toluene Trichloroethane (methyl chloroform) Trichloroethylene Vinyl ether Others/unsorted
3-Hydroxybutanal Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide , potassium bromide , sodium bromide )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole DEABL Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine , , dihydroergotamine , ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )Efavirenz Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid , mefenamic acid , niflumic acid , tolfenamic acid )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Hopantenic acid Lanthanum Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol , honokiol , magnolol , obovatol )Loreclezole Menthyl isovalerate (validolum) Monastrol Niacin Niacinamide Org 25,435 Phenytoin Propanidid Retigabine (ezogabine) Safranal Seproxetine Stiripentol (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) , tetronal , trional )
Terpenoids (e.g., borneol )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid , isovaleramide , valerenic acid , )Unsorted benzodiazepine site positive modulators: α-Pinene See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators