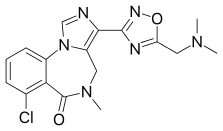
EVT-201 ATC code show 7-Chloro-3-{5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl}-5-methyl-4,5-dihydro-6H -imidazo[1,5-a ][1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider UNII Formula C 17 H 17 Cl N 6 O 2 Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol ) show Clc4cccc3n2cnc(c1nc(on1)CN(C)C)c2CN(C(=O)c34)C
show InChI=1S/C17H17ClN6O2/c1-22(2)8-13-20-16(21-26-13)15-12-7-23(3)17(25)14-10(18)5-4-6-11(14)24(12)9-19-15/h4-6,9H,7-8H2,1-3H3
Key:JCYLWUVDHLVGER-UHFFFAOYSA-N
EVT-201 is a benzodiazepine derivative drug and partial positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor .[1] affinity for the α1 subunit relative to the α2 , α3 , and α5 subunits and significantly less intrinsic activity in comparison to currently-marketed benzodiazepines and the Z-drugs .[2] insomnia , and it is thought that the lower efficacy may result in fewer side effects , such as motor incoordination .[2] Roche , based on preclinical data, as a non-sedating anxiolytic , but was found to produce sedation in humans in phase I clinical trials . For this reason, it was subsequently licensed to Evotec, which is now developing it for the treatment of insomnia.[2] phase II clinical trials for this indication, with positive findings reported.[3] Phase II development is ongoing in China .[4]
See also [ ] References [ ] External links [ ] show Insomnia pharmacotherapies
GABAA R PAMs
Benzodiazepines :Brotizolam Cinolazepam Climazolam Clorazepate Doxefazepam Estazolam Etizolam Flunitrazepam Flurazepam Flutoprazepam Haloxazolam Loprazolam Lormetazepam Midazolam Nimetazepam Nitrazepam Quazepam Temazepam Triazolam ; Nonbenzodiazepines /Z-drugs :Eszopiclone Zaleplon Zolpidem Zopiclone ; Others: Alcohols (e.g., ethchlorvynol , amylene hydrate , ethanol )Barbiturates (e.g., amobarbital , pentobarbital , phenobarbital , secobarbital )Bromides (e.g., potassium bromide , sodium bromide )Carbamates (e.g., meprobamate )Chloral hydrate Clomethiazole Kava Paraldehyde Piperidinediones (e.g., glutethimide )Quinazolinones (e.g., methaqualone )Sulfonmethane Valerian Antihistamines (H1 R inverse agonists ) OXR antagonists MTR agonists Miscellaneous
Antipsychotics (e.g., quetiapine , olanzapine , chlorpromazine )Ashwagandha Benzoctamine Cannabinoids (e.g., cannabis , dronabinol (THC ) , nabilone )Chamomile Fenadiazole Gabapentinoids (e.g., gabapentin , pregabalin , phenibut )Hops Lavender Menthyl isovalerate Niaprazine Opioids (e.g., hydrocodone , oxycodone , morphine )Passion flower Scopolamine Serotonin precursors (tryptophan , 5-HTP Sodium oxybate (GHB ) Sympatholytics (e.g., clonidine , guanfacine )TCAs amitriptyline , doxepin , trimipramine )TeCAs mirtazapine )Theanine Trazodone Valnoctamide
show GABA A receptor positive modulatorsAlcohols
Butanol Chloralodol Chlorobutanol (cloretone) Ethanol (alcohol) (alcoholic drink )Ethchlorvynol Isobutanol Isopropanol Menthol Methanol Methylpentynol Pentanol Petrichloral Propanol tert -Butanol (2M2P)tert -Pentanol (2M2B)Tribromoethanol Trichloroethanol Triclofos Trifluoroethanol Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Carbamates Flavonoids
Ampelopsin (dihydromyricetin) Apigenin Baicalein Baicalin Catechin EGC EGCG Hispidulin Luteolin Skullcap constituents (e.g., baicalin )Wogonin Imidazoles Kava constituents
Desmethoxyyangonin Kavain Methysticin Yangonin Monoureides Neuroactive steroids Nonbenzodiazepines Phenols
Fospropofol Propofol Thymol Piperidinediones Pyrazolopyridines Quinazolinones Volatiles /gases
Acetone Acetophenone Acetylglycinamide chloral hydrate Aliflurane Benzene Butane Butylene Centalun Chloral Chloral betaine Chloral hydrate Chloroform Cryofluorane Desflurane Dichloralphenazone Dichloromethane Diethyl ether Enflurane Ethyl chloride Ethylene Fluroxene Gasoline Halopropane Halothane Isoflurane Kerosine Methoxyflurane Methoxypropane Nitric oxide Nitrogen Nitrous oxide Norflurane Paraldehyde Propane Propylene Roflurane Sevoflurane Synthane Teflurane Toluene Trichloroethane (methyl chloroform) Trichloroethylene Vinyl ether Others/unsorted
3-Hydroxybutanal Avermectins (e.g., ivermectin )Bromide compounds (e.g., lithium bromide , potassium bromide , sodium bromide )Carbamazepine Chloralose Chlormezanone Clomethiazole DEABL Dihydroergolines (e.g., dihydroergocryptine , , dihydroergotamine , ergoloid (dihydroergotoxine) )Efavirenz Etazepine Etifoxine Fenamates (e.g., flufenamic acid , mefenamic acid , niflumic acid , tolfenamic acid )Fluoxetine Flupirtine Hopantenic acid Lanthanum Lavender oil Lignans (e.g., 4-O-methylhonokiol , honokiol , magnolol , obovatol )Loreclezole Menthyl isovalerate (validolum) Monastrol Niacin Niacinamide Org 25,435 Phenytoin Propanidid Retigabine (ezogabine) Safranal Seproxetine Stiripentol (e.g., sulfonmethane (sulfonal) , tetronal , trional )
Terpenoids (e.g., borneol )Topiramate Valerian constituents (e.g., isovaleric acid , isovaleramide , valerenic acid , )Unsorted benzodiazepine site positive modulators: α-Pinene See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators
show Benzodiazepines
1,4-Benzodiazepines 1,5-Benzodiazepines 2,3-Benzodiazepines* Triazolobenzodiazepines
Adinazolam Alprazolam Balovaptan *Bromazolam Clonazolam Estazolam Flualprazolam Flubromazolam Flunitrazolam Nitrazolam Phenazolam Pyrazolam Rilmazolam (active metabolite of Rilmazafone )Triazolam Imidazobenzodiazepines
Bretazenil Climazolam EVT-201 FG-8205 Flumazenil GL-II-73 Imidazenil 123 I-IomazenilL-655,708 Loprazolam Midazolam PWZ-029 Remimazolam Ro15-4513 Ro48-6791 Ro48-8684 Ro4938581 Sarmazenil SH-053-R-CH3-2′F Oxazolobenzodiazepines Thienodiazepines Thienotriazolodiazepines Thienobenzodiazepines *Pyridodiazepines Pyridotriazolodiazepines Pyrazolodiazepines Pyrrolodiazepines Tetrahydroisoquinobenzodiazepines Pyrrolobenzodiazepines *Benzodiazepine prodrugs * atypical activity profile (not GABAA receptor ligands)