36th United States Congress
| 36th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
35th ← → 37th | |
 United States Capitol (1860) | |
March 4, 1859 – March 4, 1861 | |
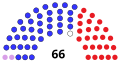
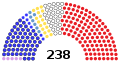
| Members | 66 senators 238 representatives 5 non-voting delegates |
| Senate Majority | Democratic (until February 4, 1861) Republican (from February 4, 1861) |
| Senate President | John C. Breckinridge (D) |
| House Majority | Republican-led coalition |
| House Speaker | William Pennington (R) |
| Sessions | |
| Special: March 4, 1859 – March 10, 1859 1st: December 5, 1859 – June 26, 1860 Special: June 26, 1860 – June 28, 1860 2nd: December 3, 1860 – March 4, 1861 | |
The 36th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1859, to March 4, 1861, during the third and fourth years of James Buchanan's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Seventh Census of the United States in 1850. The Senate had a Democratic majority, and the House had a Republican plurality.
Major events[]
- June 8, 1859: Comstock Lode discovered in the western Utah Territory (present-day Nevada)
- August 27, 1859: First oil well was drilled in the United States, near Titusville, Pennsylvania
- October 16–18, 1859: John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry
- December 2, 1859 John Brown executed.
- April 3, 1860: Pony Express began its first run
- April 23 – May 3, 1860: Democratic National Convention held in Charleston, South Carolina.[1] Unable to agree on a nominee, the delegates voted to reconvene in June.[2]
- May 9, 1860: Constitutional Union Party National Convention held in Baltimore, Maryland, nominating John Bell for president.[3]
- May 18, 1860: Republican National Convention held in Chicago, Illinois, nominating Abraham Lincoln for president.
- June 18–23, 1860: Democratic Party reconvened in Baltimore, Maryland, nominating Stephen A. Douglas for president.[2]
- June 26–28, 1860: Southern Democrats held a convention in Richmond, Virginia, nominating John C. Breckinridge for president.[2]
- November 6, 1860: U.S. presidential election: Abraham Lincoln beat John C. Breckinridge, Stephen A. Douglas, and John Bell.
- December 20, 1860: South Carolina Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[4][5]
- January 3, 1861: Delaware Secession Convention voted not to secede from the Union[6]
- January 9, 1861: Mississippi Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[7][5]
- January 10, 1861: Florida Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[8][5]
- January 11, 1861: Alabama Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[9][5]
- January 18, 1861: Georgia Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[10][5]
- January 26, 1861: Louisiana Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[11][5]
- January 29, 1861. Kansas admitted to the Union as a free state.
- February 1, 1861: Texas Secession Convention enacted an Ordinance of Secession[12][5]
- February 23, 1861: The people of Texas ratified its Ordinance of Secession[12] President-elect Abraham Lincoln arrived secretly in Washington, D.C. after an alleged assassination plot in Baltimore, Maryland.
Major legislation[]
- June 16, 1860: Pacific Telegraph Act of 1860, ch. 147, 12 Stat. 41
- March 2, 1861: Morrill Tariff, ch. 68, 12 Stat. 178
- December 18, 1860 (introduced): Crittenden Compromise, rejected by the House of Representatives and the Senate
Constitutional amendments[]
- March 2, 1861: Approved an amendment to the United States Constitution that would shield "domestic institutions" of the states (which in 1861 included slavery) from the constitutional amendment process and from abolition or interference by Congress, and submitted it to the state legislatures for ratification 12 Stat. 251
- This amendment, commonly known as the Corwin Amendment, has not been ratified and is still pending before the states.
Treaties[]
- March 8, 1859: Quinault Treaty ratified, 12 Stat. 927
- March 8, 1859: Point No Point Treaty ratified, 12 Stat. 933
States admitted and territories organized[]
- January 29, 1861: Kansas admitted as a state, ch. 20, 12 Stat. 126
- February 28, 1861: Colorado Territory organized, ch. 59, 12 Stat. 172
- March 2, 1861: Nevada Territory organized, ch. 83, 12 Stat. 209
- March 2, 1861: Dakota Territory organized, ch. 86, 12 Stat. 239
Party summary[]
Senate[]
| Party (shading shows control) |
Total | Vacant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Know Nothing (A) |
Democratic (D) | Republican (R) | Other |
|||
| End of previous congress | 4 | 42 | 20 | 0 | 66 | 0 |
| Begin | 2 | 38 | 25 | 0 | 65 | 1 |
| End | 25 | 26 | 53 | 15 | ||
| Final voting share | 3.8% | 47.2% | 49.1% | 0.0% | ||
| Beginning of next congress | 0 | 22 | 29 | 1[a] | 52 | 16 |
House of Representatives[]
| Party (shading shows control) |
Total | Vacant | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Know Nothing (A) |
Democratic (D) | Anti- Lecompton Democratic (ALD) | Independent Democratic (ID) | Opposition (O) | Republican (R) | Other |
|||
| End of previous congress | 14 | 130 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 92 | 0 | 237 | 0 |
| Begin | 5 | 83 | 8 | 7 | 19 | 113 | 0 | 235 | 2 |
| End | 59 | 7 | 17 | 115 | 210 | 28 | |||
| Final voting share | 2.4% | 28.1% | 3.3% | 3.3% | 8.1% | 54.8% | 0.0% | ||
| Beginning of next congress | 0 | 44 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 108 | 25[b] | 178 | 62 |
Leadership[]

John C. Breckinridge
Senate[]
- President: John C. Breckinridge (D)
- President pro tempore: Benjamin Fitzpatrick (D), until February 26, 1860
- Jesse D. Bright (D), June 12–13, 1860
- Benjamin Fitzpatrick (D), June 26, 1860 – December 2, 1860
- Solomon Foot (R), elected February 16, 1861
House of Representatives[]
- Speaker: William Pennington (R), elected February 1, 1860
- Democratic Caucus Chairman: George S. Houston
Members[]
This list is arranged by chamber, then by state. Senators are listed by class, and representatives are listed by district.
Senate[]
Senators were elected by the state legislatures every two years, with one-third beginning new six-year terms with each Congress. Preceding the names in the list below are Senate class numbers, which indicate the cycle of their election. In this Congress, Class 1 meant their term began in the last Congress, requiring reelection in 1862; Class 2 meant their term began with this Congress, requiring reelection in 1864; and Class 3 meant their term ended with this Congress, requiring reelection in 1860.
Alabama[]
Arkansas[]
California[]
Connecticut[]
Delaware[]
Florida[]
Georgia[]
Illinois[]
Indiana[]
Iowa[]
Kansas[]
Kentucky[]
Louisiana[]
Maine[]
Maryland[]
Massachusetts[]
Michigan[]
|
Minnesota[]
Mississippi[]
Missouri[]
New Hampshire[]
New Jersey[]
New York[]
North Carolina[]
Ohio[]
Oregon[]
Pennsylvania[]
Rhode Island[]
South Carolina[]
Tennessee[]
Texas[]
Vermont[]
Virginia[]
Wisconsin[]
|
 Senators' party membership by state at the opening of the 36th Congress in March 1859. The green stripes represent Know-Nothings. 2 Democrats 1 Democrat and 1 Republican 2 Republicans |
 President pro tempore Benjamin Fitzpatrick, until February 26, 1860 June 26, 1860 – December 2, 1860  President pro tempore Jesse D. Bright, June 12, 1860 – June 13, 1860  President pro tempore Solomon Foot, from February 16, 1861
|
House of Representatives[]
The names of members of the House of Representatives are preceded by their district numbers.
Alabama[]
Arkansas[]California[]Connecticut[]Delaware[]
Florida[]
Georgia[]
Illinois[]
Indiana[]
Iowa[]Kansas[]
Kentucky[]
Louisiana[]
Maine[]
Maryland[]
Massachusetts[]
Michigan[]
Minnesota[]Both representatives were elected statewide on a general ticket. Mississippi[]
Missouri[]
New Hampshire[]New Jersey[] |
New York[]
North Carolina[]
Ohio[]
Oregon[]
Pennsylvania[]
Rhode Island[]South Carolina[]
Tennessee[]
Texas[]Vermont[]Virginia[]
Wisconsin[]Non-voting members[]
|

 Speaker of the House William Pennington  Group photo of the U.S. House of Representatives, in 1860, during this Congress.
| ||||||||
Changes in membership[]
The count below reflects changes from the beginning of the first session of this Congress.
Senate[]
- Replacements: 4
- Democrats (D): no net change
- Republicans (R): no net change
- Deaths: 1
- Resignations: 1
- Interim appointments: 1
- Withdrawals: 13
- Total seats with changes: 16
| State (class) |
Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation[c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oregon (2) |
Vacant | Successor elected late due to legislature's failure to elect. | Edward D. Baker (R) | October 2, 1860 |
| California (1) |
David C. Broderick (D) | Died September 16, 1859, after taking part in a duel he participated in, which he was unlucky. Interim successor was appointed to continue the term. |
Henry P. Haun (D) | November 3, 1859 |
| Texas (1) |
Matthias Ward (D) | Interim appointee lost nomination to finish the term Successor elected December 5, 1859. |
Louis Wigfall (D) | December 5, 1859 |
| California (1) |
Henry P. Haun (D) | Interim appointee lost election to finish the term Successor elected March 5, 1860. |
Milton Latham (D) | March 5, 1860 |
| South Carolina (2) |
James Chesnut Jr. (D) | Withdrew November 10, 1860. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| South Carolina (3) |
James H. Hammond (D) | Withdrew November 11, 1860. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Mississippi (2) |
Albert G. Brown (D) | Withdrew January 12, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Maine (1) |
Hannibal Hamlin (R) | Resigned January 17, 1861, to become Vice President of the United States. Successor elected January 17, 1861. |
Lot M. Morrill (R) | January 17, 1861 |
| Alabama (3) |
Benjamin Fitzpatrick (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Alabama (2) |
Clement C. Clay (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Florida (1) |
Stephen Mallory (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Florida (3) |
David L. Yulee (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Mississippi (1) |
Jefferson Davis (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Georgia (3) |
Alfred Iverson Sr. (D) | Withdrew January 28, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Kansas (2) |
New seat | New state admitted to the Union January 29, 1861 Senator was not elected until the next Congress. |
Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Kansas (3) |
New seat | New state admitted to the Union January 29, 1861 Senator was not elected until the next Congress. |
Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Georgia (2) |
Robert Toombs (D) | Withdrew February 4, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Louisiana (2) |
Judah P. Benjamin (D) | Withdrew February 4, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Louisiana (3) |
John Slidell (D) | Withdrew February 4, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
| Tennessee (2) |
Alfred O. P. Nicholson (D) | Withdrew March 3, 1861. | Vacant | Not filled this Congress |
House of Representatives[]
- Replacements: 7
- Democrats (D): no net change
- Republicans (R): 1 seat net loss
- Anti-Lecompton Democrats (LD): 1 seat net gain
- Deaths: 4
- Resignations: 3
- Contested election: 1
- Withdrawals: 28
- Total seats with changes: 41
| District | Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation[c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois 6th | Vacant | Vacancy in term | John A. McClernand (D) | Seated November 8, 1859 |
| Kentucky 5th | Vacant | Brown could not take seat because he had not yet attained age required by the US Constitution | John Y. Brown (D) | Seated December 3, 1860 |
| Ohio 14th | Cyrus Spink (R) | Died May 31, 1859 | Harrison G. O. Blake (R) | Seated October 11, 1859 |
| Virginia 4th | William Goode (D) | Died July 3, 1859 | Roger A. Pryor (D) | Seated December 7, 1859 |
| Michigan 1st | George B. Cooper (D) | Lost contested election May 15, 1860 | Francis P. Blair Jr. (R) | Seated May 15, 1860 |
| Nebraska Territory At-large | Experience Estabrook | Lost contested election May 18, 1860 | Samuel G. Daily (R) | Seated May 18, 1860 |
| New York 31st | (R) | Died June 3, 1860 | Edwin R. Reynolds (R) | Seated December 5, 1860 |
| Missouri 1st | John R. Barret (D) | Lost contested election June 8, 1860 | William A. Howard (R) | Seated June 8, 1860 |
| Pennsylvania 8th | John Schwartz (ALD) | Died June 20, 1860 | Jacob K. McKenty (D) | Seated December 3, 1860 |
| Missouri 1st | William A. Howard (R) | Resigned June 25, 1860 | John R. Barret (D) | Seated December 3, 1860 |
| Mississippi 1st | Lucius Q. C. Lamar II (D) | Retired December ???, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| South Carolina 3rd | Laurence M. Keitt (D) | Retired December ???, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| South Carolina 1st | John McQueen (D) | Retired December 21, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| South Carolina 2nd | William P. Miles (D) | Retired December 21, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| South Carolina 4th | Milledge L. Bonham (D) | Retired December 21, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| South Carolina 5th | John D. Ashmore (D) | Retired December 21, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| South Carolina 6th | William W. Boyce (D) | Retired December 21, 1860 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Maine 5th | Israel Washburn Jr. (R) | Resigned January 1, 1861, after being elected Governor of Maine | Stephen Coburn (R) | Seated January 2, 1861 |
| Mississippi 2nd | Reuben Davis (D) | Withdrew January 12, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Mississippi 3rd | William Barksdale (D) | Withdrew January 12, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Mississippi 4th | Otho R. Singleton (D) | Withdrew January 12, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Mississippi 5th | John J. McRae (D) | Withdrew January 12, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Alabama 1st | James A. Stallworth (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Alabama 2nd | James L. Pugh (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Alabama 3rd | David Clopton (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Alabama 4th | Sydenham Moore (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Alabama 5th | George S. Houston (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Alabama 7th | Jabez L. M. Curry (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Florida At-large | George S. Hawkins (D) | Withdrew January 21, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 1st | Peter E. Love (D) | Retired January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 2nd | Martin J. Crawford (D) | Withdrew January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 3rd | Thomas Hardeman Jr. (O) | Withdrew January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 4th | Lucius J. Gartrell (D) | Retired January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 5th | John W. H. Underwood (D) | Withdrew January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 6th | James Jackson (D) | Retired January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 7th | Joshua Hill (O) | Resigned January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Georgia 8th | John J. Jones (D) | Withdrew January 23, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Kansas Territory At-large | Marcus J. Parrott (R) | Kansas was admitted to the Union January 29, 1861 | Seat eliminated | |
| Kansas At-large | New Seat | Kansas was admitted to the Union January 29, 1861 | Martin F. Conway (R) | Seated January 29, 1861 |
| Alabama 6th | Williamson R. W. Cobb (D) | Withdrew January 30, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Louisiana 2nd | Miles Taylor (D) | Withdrew February 5, 1861 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
Committees[]
Lists of committees and their party leaders.
Senate[]
- (Select)
- (Select)
- Audit and Control the Contingent Expenses of the Senate (Chairman: Andrew Johnson)
- (Select)
- (Select)
- Claims (Chairman: Alfred Iverson Jr.)
- Commerce (Chairman: Clement Claiborne Clay)
- (Select)
- (Select)
- District of Columbia (Chairman: Albert G. Brown)
- (Select)
- Finance (Chairman: Robert M. T. Hunter)
- Foreign Relations (Chairman: James M. Mason)
- (Select)
- (Select)
- Indian Affairs (Chairman: William K. Sebastian)
- Judiciary (Chairman: James A. Bayard Jr.)
- (Select)
- Military Affairs (Chairman: Jefferson Davis)
- Naval Affairs (Chairman: Stephen Mallory)
- (Select)
- (Select)
- Patents and the Patent Office (Chairman: William Bigler)
- Pensions (Chairman: N/A)
- Post Office and Post Roads (Chairman: N/A)
- Printing (Chairman: N/A)
- (Select)
- Private Land Claims (Chairman: N/A)
- Public Lands (Chairman: Robert W. Johnson)
- (Chairman: N/A)
- Revolutionary Claims (Chairman: N/A)
- Tariff Regulation (Select)
- Territories (Chairman: N/A)
- (Select)
- Whole
House of Representatives[]
- Accounts (Chairman: Francis E. Spinner)
- Agriculture (Chairman: Martin Butterfield)
- Claims (Chairman: John Hickman)
- Commerce (Chairman: Elihu B. Washburne)
- District of Columbia (Chairman: Luther C. Carter)
- Elections (Chairman: John A. Gilmer)
- Engraving (Chairman: Garnett B. Adrain)
- Expenditures in the Interior Department (Chairman: N/A)
- Expenditures in the Navy Department (Chairman: Robert Hatton)
- Expenditures in the Post Office Department (Chairman: George W. Palmer)
- Expenditures in the State Department (Chairman: James B. McKean)
- Expenditures in the Treasury Department (Chairman: Dwight Loomis)
- Expenditures in the War Department (Chairman: William Stewart)
- Expenditures on Public Buildings (Chairman: William D. Brayton)
- Foreign Affairs (Chairman: Thomas Corwin)
- Indian Affairs (Chairman: Emerson Etheridge)
- Invalid Pensions (Chairman: Reuben E. Fenton)
- Judiciary (Chairman: John Hickman)
- Manufactures (Chairman: Charles F. Adams)
- Mileage (Chairman: John D. Ashmore)
- Military Affairs (Chairman: Benjamin Stanton)
- Militia (Chairman: Cydnor B. Tompkins)
- Naval Affairs (Chairman: Freeman H. Morse)
- Patents (Chairman: William Millward)
- Post Office and Post Roads (Chairman: Schuyler Colfax)
- Private Land Claims (Chairman: Cadwallader C. Washburn)
- Public Buildings and Grounds (Chairman: Charles R. Train)
- Public Expenditures (Chairman: John B. Haskin)
- Public Lands (Chairman: Eli Thayer)
- Revisal and Unfinished Business (Chairman: John A. Logan)
- Revolutionary Claims (Chairman: George N. Briggs)
- Revolutionary Pensions (Chairman: John F. Potter)
- Roads and Canals (Chairman: Robert Mallory)
- Rules (Select)
- Standards of Official Conduct
- Territories (Chairman: Galusha A. Grow)
- Ways and Means (Chairman: John Sherman)
- Whole
Joint committees[]
- Enrolled Bills (Chairman: Sen. Henry Haun then Sen. Willard Saulsbury Sr.)
- The Library (Chairman: Rep. John U. Pettit)
- Printing (Chairman: Rep. John A. Gurley)
Caucuses[]
- Democratic (House)
- Democratic (Senate)
Employees[]
Legislative branch agency directors[]
- Architect of the Capitol: Thomas U. Walter
- Librarian of Congress: John Silva Meehan
Senate[]
- Chaplain: Stephen P. Hill (Baptist), until December 15, 1859
- Phineas D. Gurley (Presbyterian), elected December 15, 1859
- Secretary: Asbury Dickins
- Sergeant at Arms: Dunning R. McNair
House of Representatives[]
- Clerk: James C. Allen, until February 3, 1860
- John W. Forney, elected February 3, 1860
- Chaplain: None
- Doorkeeper: Robert B. Hackney, until February 6, 1860
- George Marston, elected February 6, 1860
- Messenger:
- Postmaster:
- Reading Clerks:[data unknown/missing]
- Sergeant at Arms: Adam J. Glossbrenner, until February 3, 1860
- Henry William Hoffman, from February 3, 1860
See also[]
- United States elections, 1858 (elections leading to this Congress)
- United States Senate elections, 1858 and 1859
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1858 and 1859
- United States elections, 1860 (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
- 1860 United States presidential election
- United States Senate elections, 1860 and 1861
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1860
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ "1860 Democratic Convention Number 1 - Charleston, South Carolina". Usgovinfo.about.com. June 19, 2010. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c "1860 Democratic National Convention". Blueandgraytrail.com. August 19, 2006. Archived from the original on November 11, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ "Constitutional Union party Facts, information, pictures | Encyclopedia.com articles about Constitutional Union party". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ "Ordinance of Secession of South Carolina". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on April 24, 2002. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Hart, Albert Bushnell; Channing, Edward, eds. (November 1893). Ordinances of Secession and Other Documents. 1860-1861. American History Leaflets Colonial and Constitutional. Vol. 12. New York: A. Lovell & Company. OCLC 7759360. Retrieved November 15, 2017. Alt URL
- ^ "The Delaware Legislature.; Reception Of The Secession Commissioner From Mississippi". The New York Times. January 4, 1861.
- ^ "Ordinance of Secession of Mississippi". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ "Ordinance of Secession of Florida". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ "Ordinance of Secession of Alabama". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on January 15, 2012. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ "Ordinance of Secession of Georgia". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ "Ordinance of Secession of Louisiana". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
- ^ a b "Ordinance of Secession of Texas". Csawardept.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved December 5, 2011.
References[]
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Hart, Albert Bushnell; Channing, Edward, eds. (November 1893). Ordinances of Secession and Other Documents. 1860-1861. American History Leaflets Colonial and Constitutional. Vol. 12. New York: A. Lovell & Company. OCLC 7759360. Retrieved November 15, 2017. Alt URL
External links[]
- Statutes at Large, 1789-1875
- Senate Journal, First Forty-three Sessions of Congress
- House Journal, First Forty-three Sessions of Congress
- Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress
- U.S. House of Representatives: House History
- U.S. Senate: Statistics and Lists
- Congressional Directory for the 36th Congress, 2nd Session.
- 36th United States Congress