Bogotá Formation
| Bogotá Formation Stratigraphic range: Late Paleocene-Early Eocene (Peligran-Casamayoran) | |
|---|---|
| Type | Geological formation |
| Underlies | Regadera Formation |
| Overlies | Cacho Formation |
| Thickness | 169–1,415 m (554–4,642 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Mudstone, shale, siltstone |
| Other | Sandstone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 4°29′18.4″N 74°08′08.5″W / 4.488444°N 74.135694°WCoordinates: 4°29′18.4″N 74°08′08.5″W / 4.488444°N 74.135694°W |
| Region | Bogotá savanna & Eastern Hills, Altiplano Cundiboyacense Eastern Ranges, Andes |
| Country | |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Bogotá |
| Named by | Hettner |
| Location | Ciudad Bolívar, Bogotá |
| Year defined | 1892 |
| Coordinates | 4°29′18.4″N 74°08′08.5″W / 4.488444°N 74.135694°W |
| Approximate paleocoordinates | 2°06′N 62°24′W / 2.1°N 62.4°W |
| Region | Cundinamarca |
| Country | |
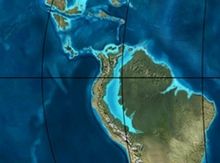 Paleogeography of Northern South America 50 Ma, by Ron Blakey | |
The Bogotá Formation (Spanish: Formación Bogotá, E1-2b, Tpb, Pgb) is a geological formation of the Eastern Hills and Bogot�� savanna on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The predominantly shale and siltstone formation, with sandstone beds intercalated, dates to the Paleogene period; Upper Paleocene to Lower Eocene epochs, with an age range of 61.66 to 52.5 Ma, spanning the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum. The thickness of the Bogotá Formation ranges from 169 metres (554 ft) near Tunja to 1,415 metres (4,642 ft) near Bogotá. Fossils of the ungulate Etayoa bacatensis have been found in the Bogotá Formation, as well as numerous reptiles, unnamed as of 2017.
Etymology[]
The formation was first described by Hettner in 1892,[1] then by in 1931, 1945 and 1957, and named in 1963 by after the Colombian capital Bogotá and its savanna.[2]
Description[]

Lithologies[]
The Bogotá Formation consists mainly of grayish-red, locally purplish, commonly greenish-gray, generally poorly stratified mudstone and silty claystone. Lithic arenite sandstone lenses, ranging from fine- to medium-grained, generally friable and variegated, are local constituents. Carbonaceous material is present as thin beds of low-grade argillaceous coal, north of Bogotá.[3][4] Fossil remains of Etaoya bacatensis, named after Colombian geologist Fernando Etayo and the indigenous name for the Bogotá savanna, Bacatá,[5] have been found in Ciudad Bolívar, close to the type locality of the Bogotá Formation.[6] Additionally, macroflora of , named after Dutch botanist Thomas van der Hammen,[7] and pollen of , and have been found, used for dating the formation.[1] Other pollen and flora, as , , , and have been found in the Bogotá Formation.[8] The abundant paleosols of the Bogotá Formation show an increase in chemical weathering across the Paleocene-Eocene (P-E) transition; the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum.[9]
Later analysis has found several other species, such as pleurodire turtles, found at the Doña Juana dump,[10] dyrosaurid mesoeucrocodylians, boid snakes, dipnoan fishes, frogs, lizards, sebecid crocodyliforms and 11 fossils of mammals.[11] The find of a derived snake in the Lower Eocene section of the formation represents the oldest New World record.[12] The finds of iguanians, including the fossil record of hoplocercines, and boine, caenophidian, and ungaliophiine snakes, indicate a tropical forest environment, present just before the (EECO).[13] The faunal distribution has been correlated to the Carodnia-, -, and -bearing of the Golfo San Jorge Basin in Patagonia, Argentina.[14]
Stratigraphy and depositional environment[]
The Bogotá Formation, with a thickness of 169 metres (554 ft) close to Tunja to 1,415 metres (4,642 ft) near Bogotá,[15][16] overlies the Cacho Formation and is overlain by the Regadera Formation. The age has been estimated to be Late Paleocene to Early Eocene.[17] The middle part of the succession has been dated using detrital zircons at 56.2 ± 1.6 Ma.[3][18] The spread of ages based on zircons has been reported from 60.96 ± 0.7 to 53.6 ± 1.1 Ma.[19] The Bogotá Formation is laterally equivalent with the , the , the ,[17] ,[20] and the fossil-rich Cerrejón Formation of La Guajira.[11]
Outcrops[]

The Bogotá Formation is apart from its type locality, found in the synclinals of the Río Frío, Checua-Lenguazaque, Sesquilé, , Subachoque,[21] around Lake Suesca, in the Tenza Valley, and in the synclinals of Teusacá and Usme.[2][22][23] In the Usme Synclinal, the formation has a thickness of 436.5 metres (1,432 ft).[24] The campus of the Universidad La Javeriana has the Bogotá Formation as solid basement rock.[25]
The Bogotá Formation forms the footwall of the eastward compressional Chicamocha Fault,[21] and the footwall of the westward thrusting Bogotá Fault.[22]
Regional correlations[]
| Ma | Age | Paleomap | Regional events | proximal Llanos | distal Llanos | Environments | Maximum thickness | Petroleum geology | Notes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | Holocene |  |
Holocene volcanism Seismic activity |
alluvium | Overburden | ||||||||
| 1 | Pleistocene |  |
Pleistocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 Glaciations |
Soatá Sabana |
Alluvial to fluvial (Guayabo) | 550 m (1,800 ft) (Guayabo) |
[26][27][28][29] | ||||||
| 2.6 | Pliocene |  |
Pliocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 GABI |
Subachoque | |||||||||
| 5.3 | Messinian | Andean orogeny 3 Foreland |
Marichuela | Honda | [28][30] | ||||||||
| 13.5 | Langhian | Regional flooding | hiatus | Lacustrine (León) | 400 m (1,300 ft) (León) |
Seal | [29][31] | ||||||
| 16.2 | Burdigalian | Miocene inundations Andean orogeny 2 |
Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C1) | 850 m (2,790 ft) (Carbonera) |
Reservoir | [30][29] | |||||||
| 17.3 | Distal lacustrine-deltaic (C2) | Seal | |||||||||||
| 19 | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C3) | Reservoir | |||||||||||
| 21 | Early Miocene | Pebas wetlands | Barzalosa | Distal fluvio-deltaic (C4) | Seal | ||||||||
| 23 | Late Oligocene |  |
Andean orogeny 1 Foredeep |
Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C5) | Reservoir | [27][30] | |||||||
| 25 | Distal fluvio-lacustrine (C6) | Seal | |||||||||||
| 28 | Early Oligocene | Proximal deltaic-marine (C7) | Reservoir | [27][30][32] | |||||||||
| 32 | Oligo-Eocene | Usme | onlap | Marine-deltaic (C8) | Seal Source |
[32] | |||||||
| 35 | Late Eocene |  |
Coastal (Mirador) | 240 m (790 ft) (Mirador) |
Reservoir | [29][33] | |||||||
| 40 | Middle Eocene | Regadera | hiatus | ||||||||||
| 45 | |||||||||||||
| 50 | Early Eocene |  |
Deltaic (Los Cuervos) | 260 m (850 ft) (Los Cuervos) |
Seal Source |
[29][33] | |||||||
| 55 | Late Paleocene | PETM 2000 ppm CO2 |
Bogotá | ||||||||||
| 60 | Early Paleocene | SALMA | Barco | Guaduas | Fluvial (Barco) | 225 m (738 ft) (Barco) |
Reservoir | [26][27][30][29][34] | |||||
| 65 | Maastrichtian |  |
KT extinction | Guadalupe | Deltaic-fluvial (Guadalupe) | 750 m (2,460 ft) (Guadalupe) |
Reservoir | [26][29] | |||||
| 72 | Campanian | End of rifting | [29][35] | ||||||||||
| 83 | Santonian | Villeta/Güagüaquí | |||||||||||
| 86 | Coniacian | ||||||||||||
| 89 | Turonian | Cenomanian-Turonian anoxic event | Chipaque | Gachetá | hiatus | Restricted marine (all) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Gachetá) |
Source | [26][29][36] | ||||
| 93 | Cenomanian |  |
Rift 2 | ||||||||||
| 100 | Albian | Une | Une | Caballos | Deltaic (Une) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Une) |
Reservoir | [30][36] | |||||
| 113 | Aptian |  |
Fómeque | Open marine (Fómeque) | 800 m (2,600 ft) (Fómeque) |
Source (Fóm) | [27][29][37] | ||||||
| 125 | Barremian | High biodiversity | Paja | Shallow to open marine (Paja) | 940 m (3,080 ft) (Paja) |
Reservoir | [26] | ||||||
| 129 | Hauterivian |  |
Rift 1 | Las Juntas | hiatus | Deltaic (Las Juntas) | 910 m (2,990 ft) (Las Juntas) |
Reservoir (LJun) | [26] | ||||
| 133 | Valanginian | Macanal Rosablanca |
Restricted marine (Macanal) | 2,935 m (9,629 ft) (Macanal) |
Source (Mac) | [27][38] | |||||||
| 140 | Berriasian | Girón | |||||||||||
| 145 | Tithonian | Break-up of Pangea | Arcabuco | Alluvial, fluvial (Buenavista) | 110 m (360 ft) (Buenavista) |
"Jurassic" | [30][39] | ||||||
| 150 | Early-Mid Jurassic |  |
Passive margin 2 | La Quinta | Noreán |
hiatus | Coastal tuff (La Quinta) | 100 m (330 ft) (La Quinta) |
[40] | ||||
| 201 | Late Triassic |  |
[30] | ||||||||||
| 235 | Early Triassic |  |
Pangea | hiatus | "Paleozoic" | ||||||||
| 250 | Permian |  |
|||||||||||
| 300 | Late Carboniferous |  |
Famatinian orogeny | () |
[41] | ||||||||
| 340 | Early Carboniferous | Fossil fish Romer's gap |
Cuche (355-385) |
() |
Deltaic, estuarine (Cuche) | 900 m (3,000 ft) (Cuche) |
|||||||
| 360 | Late Devonian |  |
Passive margin 1 | Río Cachirí (360-419) |
() |
Alluvial-fluvial-reef (Farallones) | 2,400 m (7,900 ft) (Farallones) |
[38][42][43][44][45] | |||||
| 390 | Early Devonian |  |
High biodiversity | Floresta (387-400) |
Shallow marine (Floresta) | 600 m (2,000 ft) (Floresta) |
|||||||
| 410 | Late Silurian | ||||||||||||
| 425 | Early Silurian | hiatus | |||||||||||
| 440 | Late Ordovician |  |
Rich fauna in Bolivia | (450-490) |
() |
||||||||
| 470 | Early Ordovician | First fossils | (>470±22) |
() |
() |
() |
[46][47][48] | ||||||
| 488 | Late Cambrian |  |
Regional intrusions | (490-515) |
() |
() |
(490-590) |
() |
[49][50] | ||||
| 515 | Early Cambrian | Cambrian explosion | [48][51] | ||||||||||
| 542 | Ediacaran |  |
Break-up of Rodinia | pre-Quetame | post-Parguaza | () |
Yellow: allochthonous basement (Chibcha Terrane) Green: autochthonous basement (Río Negro-Juruena Province) |
Basement | [52][53] | ||||
| 600 | Neoproterozoic |  |
Cariri Velhos orogeny | (600-1400) |
pre-Guaviare | [49] | |||||||
| 800 |  |
Snowball Earth | [54] | ||||||||||
| 1000 | Mesoproterozoic |  |
Sunsás orogeny | (1000) |
(1030-1100) |
[55][56][57][58] | |||||||
| 1300 | pre-Ariarí | (1300-1400) |
(1180-1550) |
[59] | |||||||||
| 1400 |  |
pre-Bucaramanga | [60] | ||||||||||
| 1600 | Paleoproterozoic | (1500-1700) |
pre-Garzón | [61] | |||||||||
| 1800 |  |
(1800) |
[59][61] | ||||||||||
| 1950 | pre-Mitú | [59] | |||||||||||
| 2200 | Columbia | ||||||||||||
| 2530 | Archean |  |
[59] | ||||||||||
| 3100 | Kenorland | ||||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
- Legend
- group
- important formation
- fossiliferous formation
- minor formation
- (age in Ma)
- proximal Llanos (Medina)[note 1]
- distal Llanos (Saltarin 1A well)[note 2]
Itaboraian correlations[]
| Formation | Itaboraí | Bogotá | Cerrejón | Ypresian (IUCS) • Wasatchian (NALMA) Bumbanian (ALMA) • Mangaorapan (NZ) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basin | Golfo San Jorge | Salta | Altiplano Basin | & |
Altiplano Cundiboyacense |
Cesar-Ranchería | |||
| Country | |||||||||
| Carodnia | |||||||||
| Victorlemoinea | |||||||||
| Polydolopimorphia | |||||||||
| Birds | |||||||||
| Reptiles | |||||||||
| Fish | |||||||||
| Flora | |||||||||
| Environments | Alluvial-lacustrine | Alluvial-fluvial | Fluvio-lacustrine | Lacustrine | Fluvial | Fluvio-deltaic | |||
| Volcanic | Yes | ||||||||
See also[]
- Geology of the Eastern Hills
- Geology of the Ocetá Páramo
- Geology of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense
Notes and references[]
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ a b Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.59
- ^ a b Montoya & Reyes, 2005, p.57
- ^ a b Bayona et al., 2010, p.5
- ^ McLaughlin, 1970, p.15
- ^ Villarroel, 1987, p.242
- ^ Etayoa bacatensis at Fossilworks.org
- ^ Stull et al., 2012
- ^ Herrera et al., 2014, pp.204-209
- ^ Morón et al., 2013
- ^ Cadena, 2014, p.334
- ^ a b Bloch et al., 2008
- ^ Head et al., 2011
- ^ Head et al., 2012
- ^ Woodburne et al., 2014, p.60
- ^ Bayona et al., 2013, p.8
- ^ Guerrero Uscátegui, 1992, p.5
- ^ a b Montoya & Reyes, 2005, p.60
- ^ Bayona et al., 2012, p.104
- ^ Bayona et al., 2012, p.103
- ^ Figures Bayona et al.
- ^ a b Plancha 227, 1998
- ^ a b Plancha 246, 1998
- ^ Geological Map Bogotá, 1997
- ^ Bayona et al., 2010, p.10
- ^ García & Alfaro, 2001, p.5
- ^ a b c d e f García González et al., 2009, p.27
- ^ a b c d e f García González et al., 2009, p.50
- ^ a b García González et al., 2009, p.85
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Barrero et al., 2007, p.60
- ^ a b c d e f g h Barrero et al., 2007, p.58
- ^ Plancha 111, 2001, p.29
- ^ a b Plancha 177, 2015, p.39
- ^ a b Plancha 111, 2001, p.26
- ^ Plancha 111, 2001, p.24
- ^ Plancha 111, 2001, p.23
- ^ a b Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.32
- ^ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.30
- ^ a b Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.21-26
- ^ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.28
- ^ Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.49
- ^ Plancha 303, 2002, p.27
- ^ Terraza et al., 2008, p.22
- ^ Plancha 229, 2015, pp.46-55
- ^ Plancha 303, 2002, p.26
- ^ Moreno Sánchez et al., 2009, p.53
- ^ Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.43
- ^ Manosalva Sánchez et al., 2017, p.84
- ^ a b Plancha 303, 2002, p.24
- ^ a b Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.42
- ^ Arango Mejía et al., 2012, p.25
- ^ Plancha 350, 2011, p.49
- ^ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.17-21
- ^ Plancha 111, 2001, p.13
- ^ Plancha 303, 2002, p.23
- ^ Plancha 348, 2015, p.38
- ^ Planchas 367-414, 2003, p.35
- ^ Toro Toro et al., 2014, p.22
- ^ Plancha 303, 2002, p.21
- ^ a b c d Bonilla et al., 2016, p.19
- ^ Gómez Tapias et al., 2015, p.209
- ^ a b Bonilla et al., 2016, p.22
- ^ a b Duarte et al., 2019
- ^ García González et al., 2009
- ^ Pulido & Gómez, 2001
- ^ García González et al., 2009, p.60
Bibliography[]
- , and . 2002. Mapa Geológico del Departamento de Cundinamarca - 1:250,000 - Memoria explicativa, 1-108. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; ; ; ; ; , and . 2010. Estratigrafía, procedencia, subsidencia y exhumación de las unidades paleógenas en el Sinclinal de Usme, sur de la zona axial de la Cordillera Oriental - Stratigraphy, provenance, subsidence and exhumation of the Paleogene succession in the Usme Syncline, southern axial zone of the Eastern Cordillera. Geología Colombiana 35. 5-35. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; ; ; ; ; , and . 2013. Onset of fault reactivation in the Eastern Cordillera of Colombia and proximal Llanos Basin; response to Caribbean–South American convergence in early Palaeogene time. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 377. 1-31. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; ; ; ; ; , and . 2012. Early Paleogene magmatism in the northern Andes: Insights on the effects of Oceanic Plateau–continent convergence. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 331-332. 97-111. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; , and . 2008. Vertebrate faunas from the Paleocene Bogotá Formation of northern Colombia (Abstract). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology Society of Vertebrate Paleontology, 68th Annual Meeting. _. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- . 2014. The fossil record of turtles in Colombia; a review of the discoveries, research and future challenges. Acta Biológica Colombiana, Universidad Nacional de Colombia 19. 333-339. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- , and . 2001. La prevención sísmica empieza por casa, estudios de microzonificación sísmica en el campus de la Universidad Javeriana - Bogotá - Colombia, 1-13. Congreso Nacional de Ingeniería Física, Guadalajara, Mexico. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- . 1992. Geología e Hidrogeología de Santafé de Bogotá y su Sabana, 1–20. Sociedad Colombiana de Ingenieros.
- ; ; , and . 2012. Paleogene Squamates from the Northern neotropics: Ecological Implications and Biogeographic Histories (Abstract). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 72nd Annual Meeting of the Society of vertebrate Paleontology, At Raleigh, North Carolina. _. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; , and . 2011. An enigmatic derived snake from the earliest Eocene of equatorial South America (Abstract). Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology Society of Vertebrate Paleontology, 71st Annual Meeting, Las Vegas, NV. _. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; , and . 2014. Paleocene wind-dispersed fruits and seeds from Colombia and their implications for early Neotropical rainforests. 54. 197-229. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- . 1970. Economic geology of the Zipaquirá quadrangle and adjoining area, Department of Cundinamarca, Colombia, 1-126. USGS. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- , and . 2005. Geología de la Sabana de Bogotá, 1–104. INGEOMINAS.
- ; ; ; ; ; , and . 2013. Climate change during the Early Paleogene in the Bogotá Basin (Colombia) inferred from paleosol carbon isotope stratigraphy, major oxides, and environmental magnetism (Abstract). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 388. 115-127. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; , and . 2012. Fruits of an “Old World” tribe (Phytocreneae; Icacinaceae) from the Paleogene of North and South America. Systematic Botany 37. 784–794. Accessed 2019-02-04.
- . 1987. Características y afinadas de Etayoa n. gen., tipo de una nueva familia de Xenungulata (Mammalia) del Paleoceno Medio (?) de Colombia. Comunicaciones Paleontológicas del Museo de Historia Natural de Montevideo 19. 241-254. Accessed 2017-03-29.
- ; ; ; ; ; ; , and . 2014. Paleogene Land Mammal Faunas of South America; a Response to Global Climatic Changes and Indigenous Floral Diversity. Journal of Mammalian Evolution 21. 1-73. Accessed 2017-03-29.
Maps[]
- , and . 2009. Plancha 171 - Duitama - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- , and . 2009. Plancha 190 - Chiquinquirá - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- ; , and . 1998. Plancha 191 - Tunja - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- , and . 1998. Plancha 208 - Villeta - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- , and . 2009. Plancha 209 - Zipaquirá - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- ; ; ; , and . 2010. Plancha 210 - Guateque - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- ; , and . 1998. Plancha 227 - La Mesa - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- ; , and . 1998. Plancha 228 - Santafé de Bogotá Noreste - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- , and . 1998. Plancha 246 - Fusagasugá - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- ; , and . 1999. Plancha 265 - Icononzo - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- . 1997. Mapa geológico de Santa Fe de Bogotá – Geological Map Bogotá – 1:50,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-03-16.
External links[]
- ; ; , and . 2015. Plancha 5-09 del Atlas Geológico de Colombia 2015 – escala 1:500,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2017-03-16.
- Geologic formations of Colombia
- Paleogene Colombia
- Paleocene Series of South America
- Eocene Series of South America
- Casamayoran
- Riochican
- Itaboraian
- Peligran
- Selandian Stage
- Thanetian Stage
- Ypresian Stage
- Fossiliferous stratigraphic units of South America
- Paleontology in Colombia
- Mudstone formations
- Siltstone formations
- Sandstone formations
- Shale formations
- Altiplano Cundiboyacense
- Geography of Cundinamarca Department
- Geography of Bogotá




