89th United States Congress
| 89th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
88th ← → 90th | |
 United States Capitol (1962) | |
January 3, 1965 – January 3, 1967 | |
| Members | 100 senators 435 representatives |
| Senate Majority | Democratic |
| Senate President | Vacant (until January 20, 1965) Hubert Humphrey (D) (from January 20, 1965) |
| House Majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | John W. McCormack (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 4, 1965 – October 23, 1965 2nd: January 10, 1966 – October 22, 1966 | |
The 89th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, DC from January 3, 1965, to January 3, 1967, during the second and third years of Lyndon B. Johnson's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Eighteenth Census of the United States in 1960.
Both chambers had a Democratic supermajority, and with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson to his own term in office, maintained an overall federal government trifecta.
The 89th Congress is regarded as "arguably the most productive in American history".[1] Some of its landmark legislation includes Social Security Amendments of 1965 (the creation of Medicare and Medicaid), the Voting Rights Act, Higher Education Act, and Freedom of Information Act.
Major events[]
- January 4, 1965: President Johnson proclaimed his "Great Society" during his State of the Union Address.
- January 20, 1965: Inauguration of President Lyndon B. Johnson for a full term.
- November 8, 1966: United States elections, 1966, including:
- United States Senate elections, 1966
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1966
Major legislation[]


- April 11, 1965: Elementary and Secondary Education Act, Pub.L. 89–10
- July 27, 1965: Federal Cigarette Labeling and Advertising Act, Pub.L. 89–92
- July 30, 1965: Social Security Act of 1965, Pub.L. 89–97 (including Medicaid and Medicare)
- August 6, 1965: Voting Rights Act, Pub.L. 89–110
- August 10, 1965: Housing and Urban Development Act of 1965, Pub.L. 89–117
- August 26, 1965: Public Works and Economic Development Act of 1965, Pub.L. 89–136
- September 9, 1965 Department of Housing and Urban Development Act, Pub.L. 89–174, 79 Stat. 667
- September 29, 1965: , Pub.L. 89–209
- October 3, 1965: Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, (Hart-Celler Act, INS Act) Pub.L. 89–236
- October 6, 1965: , Pub.L. 89–239
- October 20, 1965: Motor Vehicle Air Pollution Control Act, Pub.L. 89–272 (including Solid Waste Disposal Act)
- October 22, 1965: Highway Beautification Act, Pub.L. 89–285
- November 8, 1965: Higher Education Act, Pub.L. 89–329
- November 8, 1965: Amendments Pub.L. 89–333
- August 26, 1966: Laboratory Animal Welfare Act Now called the Animal Welfare Act Pub.L. 89–544
- April 13, 1966: Uniform Time Act, Pub.L. 89–387
- July 13, 1966: Cotton Research and Promotion Act, Pub.L. 89–502
- September 6, 1966: Pub.L. 89–554, which (among other things) enacted what is now called the Freedom of Information Act
- September 9, 1966: National Traffic and Motor Vehicle Safety Act, Pub.L. 89–563
- September 9, 1966: Highway Safety Act, Pub.L. 89–564
- October 15, 1966: National Historic Preservation Act, Pub.L. 89–665
- October 15, 1966: National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act of 1966, Pub.L. 89–669
- October 15, 1966: Department of Transportation Act, Pub.L. 89–670
- November 2, 1966: Cuban Adjustment Act, Pub.L. 89–732
- November 3, 1966: , Pub.L. 89–749
Constitutional amendments[]
- July 6, 1965: Approved an amendment to the United States Constitution addressing succession to the presidency and establishing procedures both for filling a vacancy in the office of the vice president, and for responding to presidential disabilities, and submitted it to the state legislatures for ratification
- Amendment was later ratified on February 10, 1967, becoming the 25th Amendment to the United States Constitution
Party summary[]
The count below identifies party affiliations at the beginning of the first session of this Congress, and includes members from vacancies and newly admitted states, when they were first seated. Changes resulting from subsequent replacements are shown below in the "Changes in membership" section.
Senate[]
| Party (shading shows control) |
Total | Vacant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (D) |
Republican (R) | |||
| End of previous congress | 66 | 34 | 100 | 0 |
| Begin | 68 | 32 | 100 | 0 |
| End | 66 | 33 | 99 | 1 |
| Final voting share | 66.7% | 33.3% | ||
| Beginning of next congress | 64 | 35 | 99 | 1 |
House of Representatives[]

| House seats by party holding plurality in state | |
|---|---|
80+% Democratic | 80+% Republican |
60+% to 80% Democratic | 60+% to 80% Republican |
Up to 60% Democratic | Up to 60% Republican |
| Party (shading shows control) |
Total | Vacant | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (D) |
Republican (R) | |||
| End of previous congress | 253 | 177 | 430 | 5 |
| Begin | 295 | 140 | 435 | 0 |
| End | 288 | 137 | 425 | 10 |
| Final voting share | 67.8% | 32.2% | ||
| Beginning of next congress | 248 | 187 | 435 | 0 |
Leadership[]

Senate[]
- President: Hubert Humphrey (D), starting January 20, 1965
- President pro tempore: Carl Hayden (D)
- Permanent Acting President pro tempore: Lee Metcalf (D)
Majority (Democratic) leadership[]
- Majority Leader and Democratic Conference Chairman: Mike Mansfield
- Majority Whip: Russell B. Long
- Caucus Secretary: George Smathers
Minority (Republican) leadership[]
- Minority Leader: Everett Dirksen
- Minority Whip: Thomas Kuchel
- Republican Conference Chairman: Leverett Saltonstall
- Republican Conference Secretary: Milton Young
- National Senatorial Committee Chair: Thruston Ballard Morton
- Policy Committee Chairman: Bourke B. Hickenlooper
House of Representatives[]
- Speaker: John W. McCormack (D)
Majority (Democratic) leadership[]
- Majority Leader: Carl Albert
- Majority Whip: Hale Boggs
- Democratic Caucus Chairman: Eugene James Keogh
- Democratic Caucus Secretary: Leonor Sullivan
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Michael J. Kirwan
Minority (Republican) leadership[]
- Minority Leader: Gerald Ford
- Minority Whip: Leslie C. Arends
- Republican Conference Chairman: Melvin Laird
- Policy Committee Chairman: John Jacob Rhodes
- Republican Campaign Committee Chairman: Bob Wilson
Caucuses[]
- House Democratic Caucus
- Senate Democratic Caucus
Members[]
This list is arranged by chamber, then by state. Senators are listed in order of seniority, and representatives are listed by district.
Senate[]
Senators are popularly elected statewide every two years, with one-third beginning new six-year terms with each Congress. Preceding the names in the list below are Senate class numbers, which indicate the cycle of their election. In this Congress, Class 1 meant their term began in this Congress, requiring reelection in 1970; Class 2 meant their term ended with this Congress, requiring reelection in 1966; and Class 3 meant their term began in the last Congress, requiring reelection in 1968.
Alabama[]
Alaska[]
Arizona[]
Arkansas[]
California[]
Colorado[]
Connecticut[]
Delaware[]
Florida[]
Georgia[]
Hawaii[]
Idaho[]
Illinois[]
Indiana[]
Iowa[]
Kansas[]
Kentucky[]
Louisiana[]
Maine[]
Maryland[]
Massachusetts[]
Michigan[]
Minnesota[]
Mississippi[]
Missouri[]
Montana[]
|
Nebraska[]
Nevada[]
New Hampshire[]
New Jersey[]
New Mexico[]
New York[]
North Carolina[]
North Dakota[]
Ohio[]
Oklahoma[]
Oregon[]
Pennsylvania[]
Rhode Island[]
South Carolina[]
South Dakota[]
Tennessee[]
Texas[]
Utah[]
Vermont[]
Virginia[]
Washington[]
West Virginia[]
Wisconsin[]
Wyoming[]
|
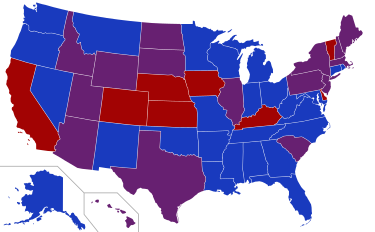 Senators' party membership by state at the opening of the 89th Congress in January 1965 2 Democrats 1 Democrat and 1 Republican 2 Republicans |
 Senate President Hubert Humphrey  Senate President pro tempore Carl Hayden  Senate Majority leader Mike Mansfield  Senate Minority leader Everett Dirksen
|
House of Representatives[]
Names of members are preceded by their district numbers.
Alabama[]
Alaska[]
Arizona[]Arkansas[]
California[]
Colorado[]Connecticut[]
Delaware[]
Florida[]
Georgia[]
Hawaii[]Idaho[]Illinois[]
Indiana[]
Iowa[]
Kansas[]
Kentucky[]
Louisiana[]
Maine[]Maryland[]
Massachusetts[]
Michigan[]
Minnesota[]
Mississippi[]
Missouri[]
Montana[] |
Nebraska[]Nevada[]
New Hampshire[]New Jersey[]
New Mexico[]New York[]
North Carolina[]
North Dakota[]Ohio[]
Oklahoma[]
Oregon[]Pennsylvania[]
Rhode Island[]South Carolina[]
South Dakota[]Tennessee[]
Texas[]
Utah[]Vermont[]
Virginia[]
Washington[]
West Virginia[]
Wisconsin[]
Wyoming[]
Non-voting member[]
|
 House Speaker John W. McCormack  House Speaker John W. McCormack (standing), speaking at a Department of Defense luncheon, February 1966.  House Majority leader Carl Albert with President Johnson  House Majority whip Hale Boggs with President Johnson
|
Changes in membership[]
Senate[]
- Replacements: 5
- Democratic: 1-seat net loss
- Republican: 1-seat net gain
- Deaths: 2
- Resignations: 2
| State (class) |
Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Carolina (3) |
Olin D. Johnston (D) | Died April 18, 1965. Successor appointed April 22, 1965 to continue the term. |
Donald S. Russell (D) | April 22, 1965 |
| Virginia (1) |
Harry F. Byrd (D) | Resigned November 10, 1965. Successor appointed November 12, 1965 to continue his father's term. |
Harry F. Byrd Jr. (D) | November 12, 1965 |
| Michigan (2) |
Patrick V. McNamara (D) | Died April 30, 1966. Successor appointed May 11, 1966 to finish the term. |
Robert P. Griffin (R) | May 11, 1966 |
| South Carolina (3) |
Donald S. Russell (D) | Interim appointee lost nomination to finish the term. Successor elected November 8, 1966. |
Fritz Hollings (D) | November 9, 1966 |
| Virginia (2) |
Absalom Willis Robertson (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966, having lost renomination. Successor appointed to finish the term, having already been elected to the next term. |
William B. Spong Jr. (D) | December 31, 1966 |
| Tennessee (2) |
Ross Bass (D) | Resigned January 2, 1967, having lost renomination. Seat remained vacant until the end of the term (the next day). |
Vacant | Not filled this term |
House of Representatives[]
- Replacements: 9
- Democratic: no net change
- Republican: no net change
- Deaths: 5
- Resignations: 15
- Total seats with changes: 20
| District | Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Carolina 2nd | Albert Watson (D) | Resigned February 1, 1965, after being stripped of seniority by the House Democratic Caucus for supporting Republican Presidential candidate Barry Goldwater. Was re-elected as a Republican in a special election to replace himself. | Albert Watson (R) | June 15, 1965 |
| Louisiana 7th | T. Ashton Thompson (D) | Died July 1, 1965 | Edwin Edwards (D) | October 2, 1965 |
| Ohio 7th | Clarence J. Brown (R) | Died August 23, 1965 | Bud Brown (R) | November 2, 1965 |
| California 26th | James Roosevelt (D) | Resigned September 30, 1965, to become the US Representative to the United Nations Economic and Social Council | Thomas M. Rees (D) | December 15, 1965 |
| North Carolina 1st | Herbert Covington Bonner (D) | Died November 7, 1965 | Walter B. Jones Sr. (D) | February 5, 1966 |
| New York 17th | John Lindsay (R) | Resigned December 31, 1965, after being elected Mayor of New York City | Theodore R. Kupferman (R) | February 8, 1966 |
| Arkansas 4th | Oren Harris (D) | Resigned February 3, 1966, to become judge of the US Court of the Eastern and Western Districts of Arkansas | David Pryor (D) | November 8, 1966 |
| Texas 8th | Albert Thomas (D) | Died February 15, 1966 | Lera Millard Thomas (D) | March 26, 1966 |
| California 14th | John F. Baldwin Jr. (R) | Died March 9, 1966 | Jerome Waldie (D) | June 7, 1966 |
| Michigan 9th | Robert P. Griffin (R) | Resigned May 10, 1966, after being appointed to the U.S. Senate | Guy Vander Jagt (R) | November 8, 1966 |
| Alaska at-large | Ralph Julian Rivers (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | Vacant | Not filled this term |
| Indiana 8th | Winfield K. Denton (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| Indiana 10th | Ralph Harvey (R) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| New York 29th | Leo W. O'Brien (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| North Carolina 4th | Harold D. Cooley (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| Ohio 15th | Robert T. Secrest (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| Pennsylvania 9th | Paul B. Dague (R) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| Pennsylvania 16th | John C. Kunkel (R) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| Tennessee 7th | Tom J. Murray (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 | ||
| Texas 9th | Clark W. Thompson (D) | Resigned December 30, 1966 |
Committees[]
Lists of committees and their party leaders, for members (House and Senate) of the committees and their assignments, go into the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of the article and click on the link (2 links), in the directory after the pages of terms of service, you will see the committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and after the committee pages, you will see the House/Senate committee assignments in the directory, on the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
Senate[]
- Aeronautical and Space Sciences (Chairman: Clinton P. Anderson; Ranking Member: Margaret Chase Smith)
- Agriculture and Forestry (Chairman: Allen J. Ellender; Ranking Member: George D. Aiken)
- Appropriations (Chairman: Carl Hayden; Ranking Member: Leverett Saltonstall)
- Armed Services (Chairman: Richard B. Russell; Ranking Member: Leverett Saltonstall)
- Banking and Currency (Chairman: A. Willis Robertson; Ranking Member: Wallace F. Bennett)
- Commerce (Chairman: Warren G. Magnuson; Ranking Member: Norris Cotton)
- District of Columbia (Chairman: Alan Bible; Ranking Member: Winston L. Prouty)
- Finance (Chairman: Russell B. Long; Ranking Member: John J. Williams)
- Foreign Relations (Chairman: J. William Fulbright; Ranking Member: Bourke B. Hickenlooper)
- Government Operations (Chairman: John Little McClellan; Ranking Member: Karl E. Mundt)
- Interior and Insular Affairs (Chairman: Henry M. Jackson; Ranking Member: Thomas H. Kuchel)
- Judiciary (Chairman: James O. Eastland; Ranking Member: Everett Dirksen)
- Labor and Public Welfare (Chairman: J. Lister Hill; Ranking Member: Jacob K. Javits)
- (Select) (Chairman:[data unknown/missing])
- Post Office and Civil Service (Chairman: A.S. Mike Monroney; Ranking Member: Frank Carlson)
- Public Works (Chairman: Pat McNamara; Ranking Member: John Sherman Cooper)
- Rules and Administration (Chairman: B. Everett Jordan; Ranking Member: Carl T. Curtis)
- Small Business (Select) (Chairman: John J. Sparkman)
- Standards and Conduct (Select) (Chairman:[data unknown/missing]; Ranking Member:[data unknown/missing])
- Whole
House of Representatives[]
- Agriculture (Chairman: Harold D. Cooley; Ranking Member: Paul B. Dague)
- Appropriations (Chairman: George H. Mahon; Ranking Member: Frank T. Bow)
- Armed Services (Chairman: L. Mendel Rivers; Ranking Member: William H. Bates)
- Banking and Currency (Chairman: Wright Patman; Ranking Member: William B. Widnall)
- District of Columbia (Chairman: John L. McMillan; Ranking Member: Ancher Nelsen)
- Education and Labor (Chairman: Adam Clayton Powell; Ranking Member: William H. Ayres)
- Foreign Affairs (Chairman: Thomas E. Morgan; Ranking Member: Frances P. Bolton)
- Government Operations (Chairman: William L. Dawson; Ranking Member: Clarence J. Brown)
- House Administration (Chairman: Omar Burleson; Ranking Member: Glenard P. Lipscomb)
- Interior and Insular Affairs (Chairman: Wayne N. Aspinall; Ranking Member: John P. Saylor)
- Interstate and Foreign Commerce (Chairman: Oren Harris; Ranking Member: William L. Springer)
- Judiciary (Chairman: Emanuel Celler; Ranking Member: William M. McCulloch)
- Merchant Marine and Fisheries (Chairman: Edward A. Garmatz; Ranking Member: William S. Mailliard)
- Post Office and Civil Service (Chairman: Tom J. Murray; Ranking Member: Robert J. Corbett)
- Public Works (Chairman: George Hyde Fallon; Ranking Member: William C. Cramer)
- Rules (Chairman: Howard W. Smith; Ranking Member: Clarence J. Brown)
- Science and Astronautics (Chairman: George Paul Miller; Ranking Member: Joseph W. Martin Jr.)
- (Select) (Chairman: Joe L. Evins)
- Standards of Official Conduct (Chairman:[data unknown/missing])
- Un-American Activities (Chairman: Edwin E. Willis; Ranking Member: John M. Ashbrook)
- Veterans' Affairs (Chairman: Olin E. Teague; Ranking Member: E. Ross Adair)
- Ways and Means (Chairman: Wilbur D. Mills; Ranking Member: John W. Byrnes)
- Whole
Joint committees[]
- Atomic Energy (Chairman: Rep. Chet Holifield; Vice Chairman: Sen. John O. Pastore)
- Conditions of Indian Tribes (Special)
- (Chairman: Sen. A. Willis Robertson; Vice Chairman: Rep. Wright Patman)
- Economic (Chairman: Rep. Wright Patman; Vice Chairman: Sen. Paul H. Douglas)
- (Chairman: Rep. Michael A. Feighan)
- The Library (Chairman: Rep. Omar Burleson; Vice Chairman: Sen. B. Everett Jordan)
- Printing (Chairman: Sen. Carl Hayden; Vice Chairman: Rep. Omar Burleson)
- (Chairman: Vacant; Vice Chairman: Vacant)
- Taxation (Chairman: Rep. Wilbur D. Mills; Vice Chairman: Sen. Harry F. Byrd)
Employees[]
Legislative branch agency directors[]
- Architect of the Capitol: J. George Stewart
- Attending Physician of the United States Congress: George Calver, until 1966
- Rufus Pearson, from 1966
- Comptroller General of the United States: Joseph Campbell, until July 31, 1965, vacant thereafter
- vacant, July 31, 1965 – March 8, 1966
- Elmer B. Staats, from March 8, 1966
- Librarian of Congress: Lawrence Quincy Mumford
- Public Printer of the United States: James L. Harrison
Senate[]
- Chaplain: Frederick Brown Harris (Methodist)
- Parliamentarian: Floyd Riddick
- Secretary: , until December 30, 1965
- Emery L. Frazier, January 1, 1966 – September 30, 1966
- Francis R. Valeo, from October 1, 1966
- Librarian:
- Democratic Party Secretary: Francis R. Valeo, until 1966
- J. Stanley Kimmitt, from 1966
- Republican Party Secretary:
- Sergeant at Arms: , until December 30, 1965
- , from January 14, 1966
House of Representatives[]
- Chaplain: Bernard Braskamp (Presbyterian)
- Clerk: Ralph R. Roberts
- Doorkeeper: William M. Miller
- Postmaster:
- Parliamentarian: Lewis Deschler
- Reading Clerks: (D) and (R)
- Sergeant at Arms:
Footnotes[]
- ^ Karen Tumulty (April 9, 2014). "LBJ's presidency gets another look as civil rights law marks its 50th anniversary". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 9, 2014.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
See also[]
- United States elections, 1964 (elections leading to this Congress)
- 1964 United States presidential election
- United States Senate elections, 1964
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1964
- United States elections, 1966 (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
- United States Senate elections, 1966
- United States House of Representatives elections, 1966
Notes[]
References[]
- Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress
- U.S. House of Representatives: Congressional History
- U.S. Senate: Statistics and Lists
External links[]
- House of Representatives Session Calendar for the 89th Congress (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 20, 2018. Retrieved June 6, 2016.
- Official Congressional Directory for the 89th Congress, 1st Session.
- Official Congressional Directory for the 89th Congress, 2nd Session.
- Pocket Congressional Directory for the 89th Congress.
- 89th United States Congress